Some people experience symptoms every month before their period: stomach cramps, muscle pain, changes in mood, etc. Constipation before your period is another common symptom of premenstrual syndrome (PMS). Read on for more information about the causes of premenstrual constipation and popular remedies.
-
Tracking cycle
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Help Center
-
Flo for Partners
-
Anonymous Mode
-
Flo app reviews
-
Flo Premium New
-
Secret Chats New
-
Symptom Checker New
-
Your cycle
-
Health 360°
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Being a mom
-
LGBTQ+
-
Quizzes
-
Ovulation calculator
-
hCG calculator
-
Pregnancy test calculator
-
Menstrual cycle calculator
-
Period calculator
-
Implantation calculator
-
Pregnancy weeks to months calculator
-
Pregnancy due date calculator
-
IVF and FET due date calculator
-
Due date calculator by ultrasound
-
Medical Affairs
-
Science & Research
-
Pass It On Project New
-
Privacy Portal
-
Press Center
-
Flo Accuracy
-
Careers
-
Contact Us
Constipation Before Your Period: Causes and Treatments


Every piece of content at Flo Health adheres to the highest editorial standards for language, style, and medical accuracy. To learn what we do to deliver the best health and lifestyle insights to you, check out our content review principles.
Reasons for premenstrual constipation
Progesterone is usually to blame for constipation before your period. Levels of this particular hormone spike before the onset of monthly menstruation, and it slows down the digestive system.
Immediately after ovulation, progesterone (which is a natural muscle relaxant) drastically increases. This essentially leads to constipation by delaying the movement of food through the bowels.
Thankfully, PMS constipation typically gets better once menstruation actually begins. This is a direct result of a rapid drop in progesterone levels during your period. Some people experience temporary diarrhea when this happens, since the hormone previously responsible for slowing down the digestive system is suddenly absent.
Another contributing factor for PMS diarrhea is a sudden boost of prostaglandins — a hormone-like substance produced by the endometrial cells. If present in extremely large amounts, prostaglandins may find their way into the muscles lining the bowels. While there, they encourage the intestines to contract and move the bowels very quickly.
How to treat constipation before your period
Whether or not it happens during your period, increasing fiber intake is usually a good treatment for constipation. It may be helpful to eat meals that include whole wheat breads, high-fiber cereals, and a wide assortment of fresh fruits and vegetables. Avoid fatty, sugary foods, and drink plenty of fluids to maintain regularity.
Exercise and other forms of physical activity might also be helpful in preventing constipation. Movement improves blood and oxygen circulation, which helps keep the bowels active. Regular exercise not only alleviates constipation before your period, it could tackle other premenstrual symptoms as well.
Remember that you can log changes in bowel movements, such as constipation, diarrhea, and bloating, in the Flo app. This makes it easy to spot any correlations between these conditions and whatever stage of the menstrual cycle you’re currently in.
If the tips above fail to relieve PMS constipation and you’re still having irregular bowel movements, seek medical attention. A health care provider will be able to investigate potential digestive disorders.
Take a quiz
Find out what you can do with our Health Assistant
Hey, I'm Anique
I started using Flo app to track my period and ovulation because we wanted to have a baby.
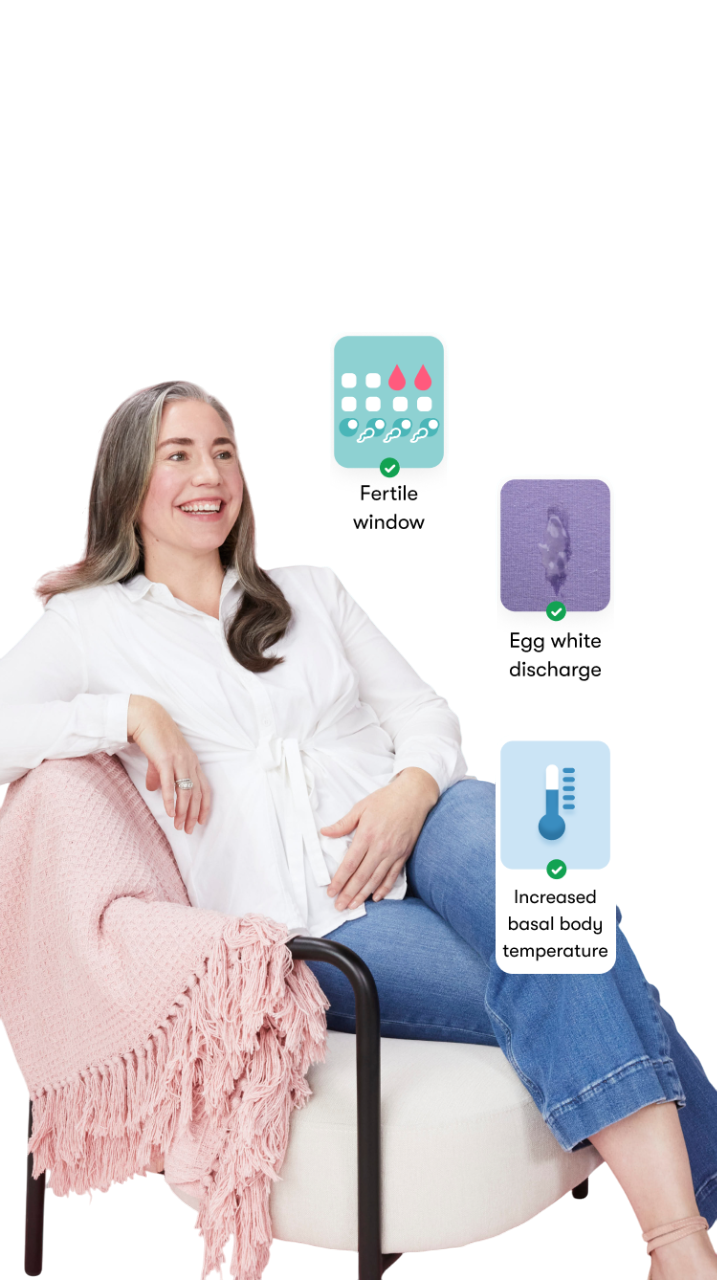

The Flo app helped me learn about my body and spot ovulation signs during our conception journey.


I vividly
remember the day
that we switched
Flo into
Pregnancy Mode — it was
such a special
moment.
Real stories, real results
Learn how the Flo app became an amazing cheerleader for us on our conception journey.




