-
Tracking cycle
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Help Center
-
Flo for Partners
-
Anonymous Mode
-
Flo app reviews
-
Flo Premium New
-
Secret Chats New
-
Symptom Checker New
-
Your cycle
-
Health 360°
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Being a mom
-
LGBTQ+
-
Quizzes
-
Ovulation calculator
-
hCG calculator
-
Pregnancy test calculator
-
Menstrual cycle calculator
-
Period calculator
-
Implantation calculator
-
Pregnancy weeks to months calculator
-
Pregnancy due date calculator
-
IVF and FET due date calculator
-
Due date calculator by ultrasound
-
Medical Affairs
-
Science & Research
-
Pass It On Project New
-
Privacy Portal
-
Press Center
-
Flo Accuracy
-
Careers
-
Contact Us
Cystitis Symptoms and Risk Factors + 6 Simple Rules That Can Help you Prevent it

Every piece of content at Flo Health adheres to the highest editorial standards for language, style, and medical accuracy. To learn what we do to deliver the best health and lifestyle insights to you, check out our content review principles.
Cystitis: symptoms and causes
Cystitis is a bladder inflammation, which can be infectious and non-infectious in nature. About 20–40% of women experience it in their lifetime.
Most often, cystitis is caused by an infection, when the bacterium Escherichia coli enters the bladder through the urethra (a tubular organ) and multiplies there.
Cystitis symptoms include:
- frequent and/or painful urination
- itching
- cloudy, strong-smelling or odorless urine
- lower abdominal pain
- occasional blood in the urine
Cystitis caused by an infection is treated with antibacterial drugs. If it is non-infectious in nature, the treatment depends on the cystitis causes. In either case, it is better to consult a doctor to speed up the recovery.
Cystitis risk factors
Itching, burning, frequent, and painful urination are the typical manifestations of bladder and urinary tract inflammation.
Cystitis is more common in women than in men due to their physiology. The female urethra is shorter, which makes it easier for the infection to reach the bladder.
Risk factors for cystitis include:
- frequent vigorous sex (“honeymoon cystitis”)
- infrequent urination, as well as restraining the urge to urinate
- pregnancy (as a result of hormonal changes)
- some STIs (chlamydia, gonorrhea, etc.)
- skin allergies to ingredients contained in soap, vaginal creams, or other products used for intimate hygiene
- the onset of menopause.
Take a quiz
Find out what you can do with our Health Assistant

Cystitis prevention
Cystitis and urinary tract infections can cause discomfort. As a prevention for urinary tract infection, it is recommended that you:
- drink more water. This helps remove unnecessary substances from the body.
- urinate more often. Go the toilet whenever you feel like it (preferably once every 2 hours) and try to empty the bladder completely.
- use toilet paper, wiping from the urethra to the anus to prevent infection
- empty the bladder after sexual intercourse
- take a shower rather than a bath
- don’t use soap, especially perfumed ones, for intimate hygiene, as it can cause irritation
Cystitis is, of course, unpleasant. But it’s not impossible to prevent if you follow certain rules! If you start to feel discomfort, though, you should consult a doctor.
Hey, I'm Anique
I started using Flo app to track my period and ovulation because we wanted to have a baby.
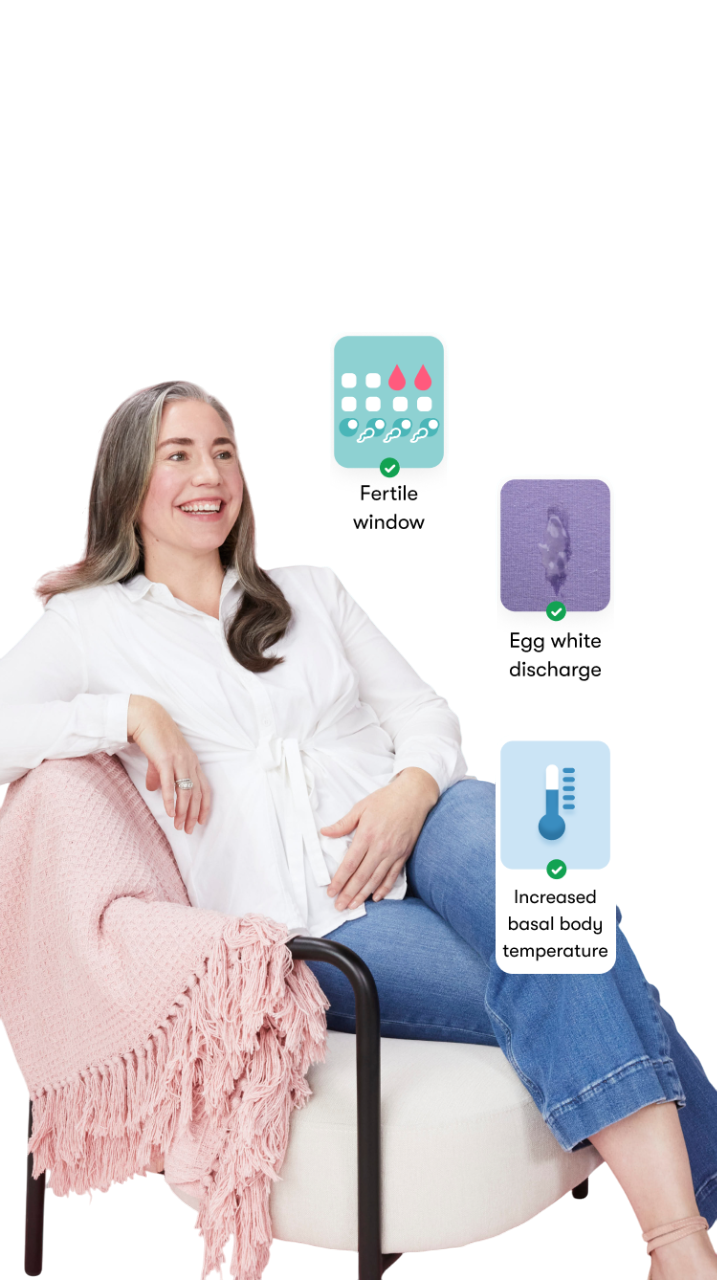

The Flo app helped me learn about my body and spot ovulation signs during our conception journey.
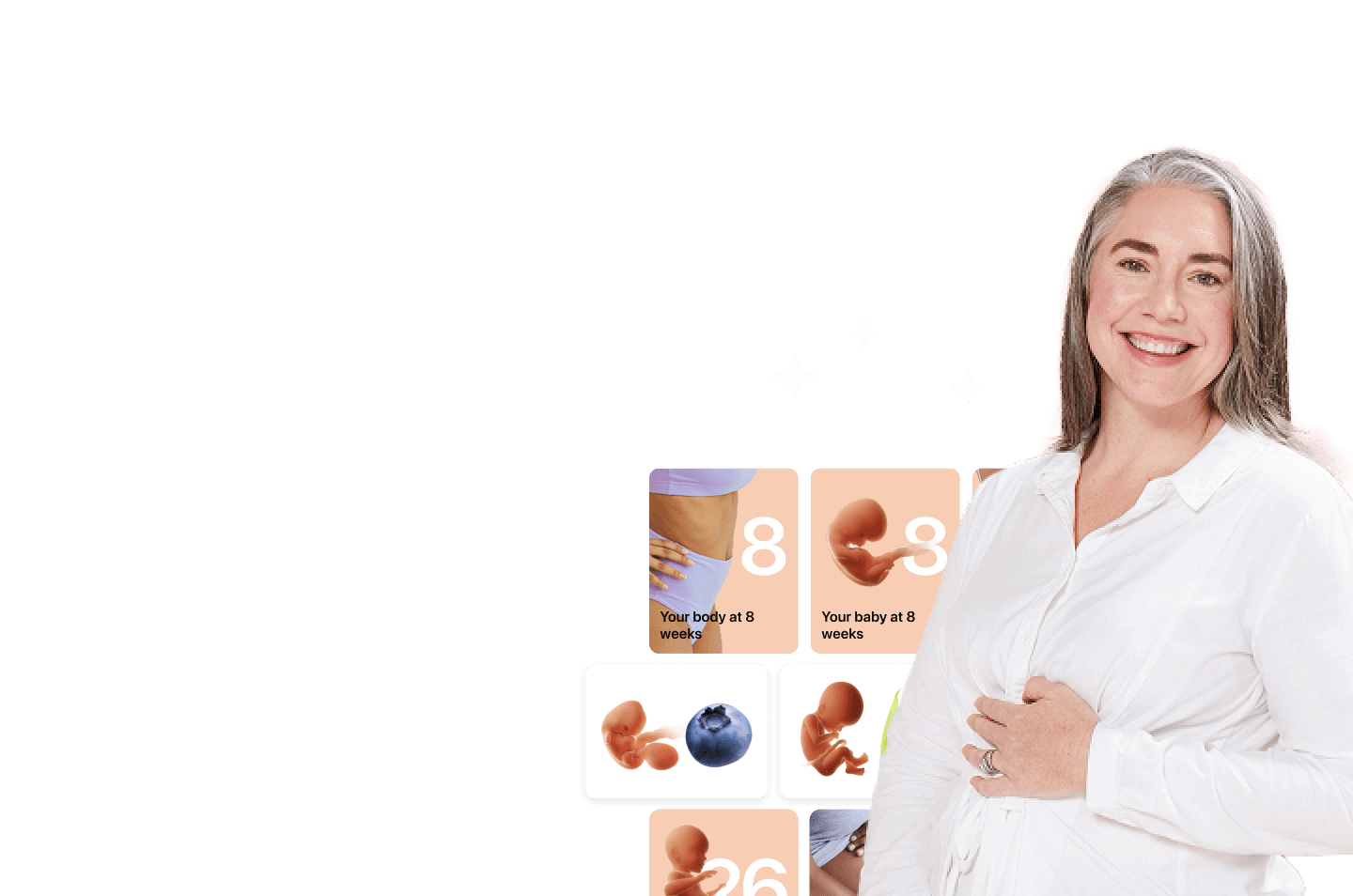
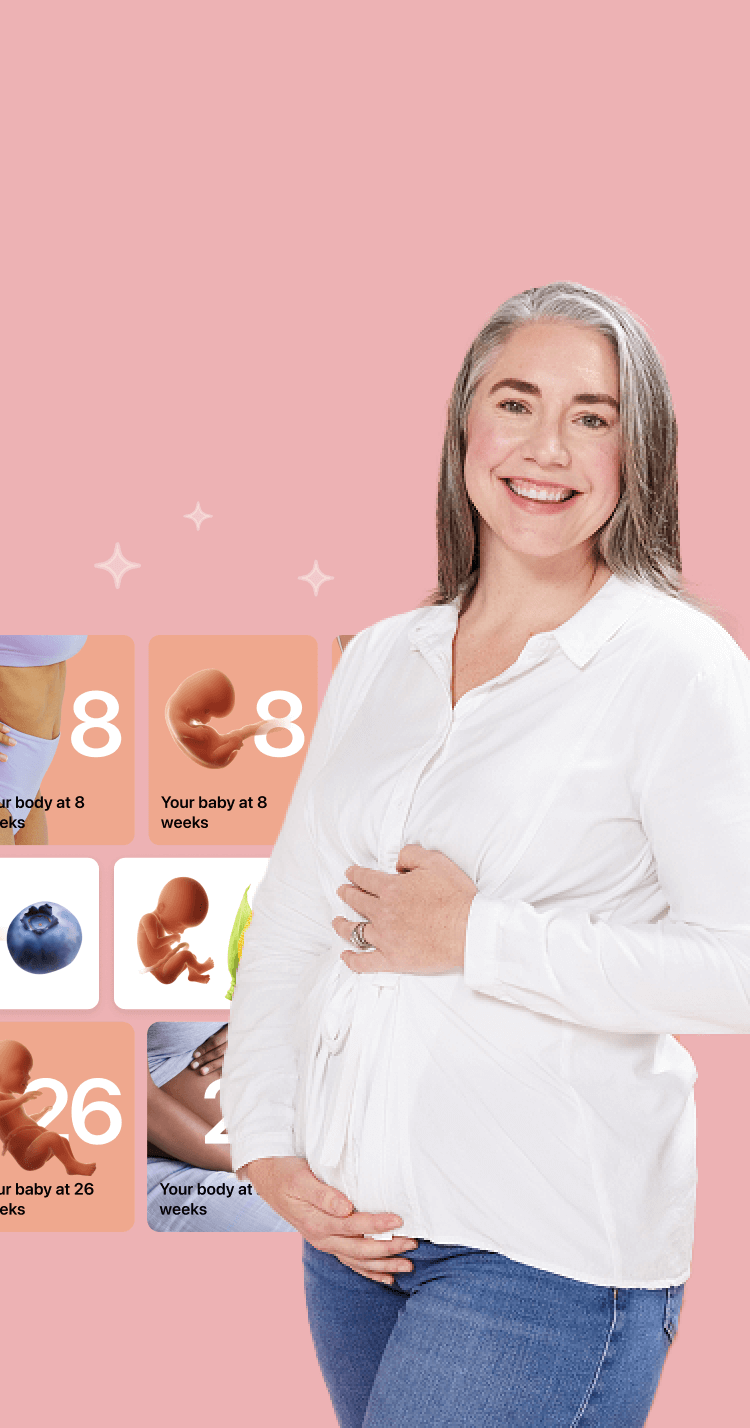


I vividly
remember the day
that we switched
Flo into
Pregnancy Mode — it was
such a special
moment.
Real stories, real results
Learn how the Flo app became an amazing cheerleader for us on our conception journey.




