Birth control quiz: Test your knowledge about the different types of contraception
You’ve probably considered using birth control at some point in your life. In fact, research from the United States shows that almost every woman (99%) aged 15–44 has used some form of contraception before. That’s a lot!
You already know that birth control can have a big impact on your life, whether you’re using it to prevent a pregnancy or for another reason, such as managing a medical condition. But what do you really know about contraception itself, from the different types available to the effectiveness of each method? Take our fun quiz to test your knowledge. Who knows, you might even learn something that could change your life for the better!
Disclaimer: This quiz is designed to help you learn more about hormonal and nonhormonal birth control methods, but it is for educational purposes only. There are many different types and brands of birth control that might work slightly differently from one another. Equally, each form of birth control can affect individuals differently. If you have any questions or concerns about which birth control method is right for you, always contact your health care provider for advice.
Start Quiz
Which of these is a hormonal birth control method?
External (male) and internal (female) condoms
Next
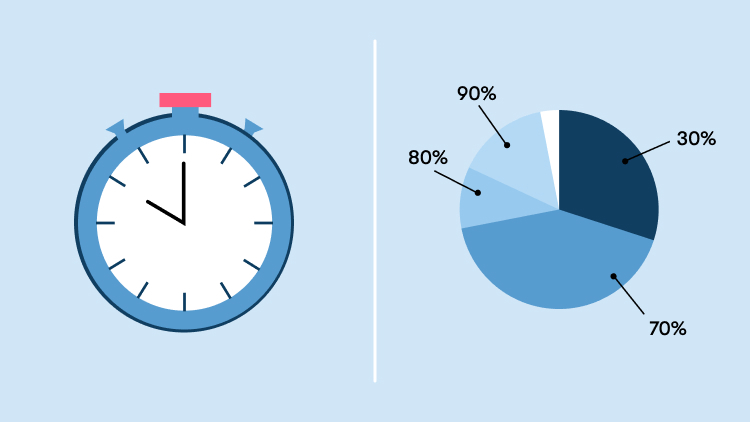
Which of the following is the most effective birth control method for preventing pregnancy?
Next
What is a barrier method of birth control?
A method that stops sperm from entering your uterus
A method that stops you from ovulating
A method that stops sperm from being released by a penis
A method that prevents sex from taking place
Next
What’s the difference between the minipill and the combined pill?
The minipill is much smaller than the combined pill.
You only take the minipill once a month, but you take the combined pill every day.
The minipill only contains progestin, while the combined pill contains progestin and estrogen.
The minipill is one pill that you take every day, while the combined pill refers to two pills that you take every day.
Next
How long can a copper IUD stay in your uterus before it needs to be removed?
Next
Which of the following forms of contraception won’t affect ovulation?
Next
Which form of birth control can also be used as emergency contraception?
Next
How effective is the withdrawal method?
Next
What parts of the body is the birth control shot usually injected into?
Next
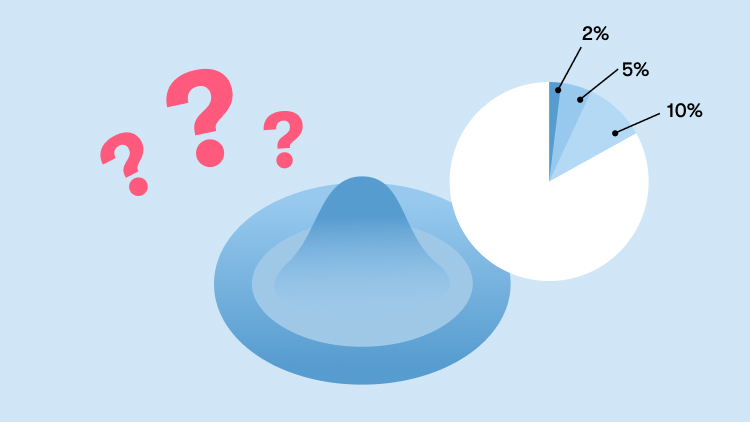
How often are external condoms thought to slip or break during sex?
Next
Which birth control method do you need to see a health care provider for?
Next
{"showCounter":false,"counterAnswers":"","correctTitle":"Correct Answer","noCorrectTitle":"Not really","allIDCorrect":false,"questions":[{"question":0,"correctAnswer":1,"answerDescription":"<p><span style=\"background-color:transparent;color:rgb(0,0,0);\">There are many different types of hormonal and nonhormonal birth control methods. The birth control shot is a hormonal method because it contains progestin (the synthetic form of the natural hormone progesterone). This can work to prevent ovulation from happening, meaning you don\u2019t release any eggs, while also thickening the cervical mucus, which makes it more difficult for sperm to reach any eggs that are released. Other examples of hormonal birth control methods include the pill, the birth control implant, hormonal (i.e., not copper) intrauterine devices (IUDs), the vaginal ring, and the patch. Condoms, sterilization, and the withdrawal method are all nonhormonal methods because they don\u2019t contain any hormones. Other examples of nonhormonal birth control include natural family planning, spermicide, diaphragms, copper IUDs, cervical caps, and the sponge. Yep, there truly are a lot of different options out there!<\/span><br><br> <\/p>"},{"question":1,"correctAnswer":2,"answerDescription":"<p><span style=\"background-color:transparent;color:rgb(0,0,0);\">Those using the implant have just a 0.05% chance of getting pregnant, which is pretty impressive. Following this, people with IUDs inserted (both copper IUDs and hormonal IUDs) have a 0.2<\/span><span style=\"background-color:transparent;color:rgb(59,62,77);\">\u2013<\/span><span style=\"background-color:transparent;color:rgb(0,0,0);\">0.8% chance of getting pregnant. Those using external condoms have an 18% chance of pregnancy, and those using spermicide have a 28% chance of pregnancy. There are plenty more options available that range in effectiveness (both more and less effective than the ones we\u2019ve listed here), so speak with your doctor about which method might be best for you. <\/span><\/p>"},{"question":2,"correctAnswer":0,"answerDescription":"<p><span style=\"background-color:transparent;color:rgb(0,0,0);\">A barrier method is a form of birth control that works by preventing sperm from entering your uterus and fertilizing an egg. Barrier methods include both male and female condoms, spermicide, diaphragms, cervical caps, and the sponge. You need to remember to use these every time you have sex if you want to prevent pregnancy. Some barrier methods also provide protection against sexually transmitted infections (STIs), making them doubly safe. Male, or external, condoms provide the most protection, but female, or internal, condoms \u2014 as well as diaphragms or cervical caps used with spermicide \u2014 can also offer some protection against some STIs. The sponge and spermicide don\u2019t provide any protection against STIs when used on their own. <\/span><\/p>"},{"question":3,"correctAnswer":2,"answerDescription":"<p><span style=\"background-color:transparent;color:rgb(0,0,0);\">The minipill and the combined pill are both hormonal methods of contraception, but the minipill only contains progestin, while the combined pill contains both estrogen and progestin (that name makes sense now, right?). To be effective, you need to take the combined pill or the minipill every day, ideally at the same time. Both types of pills are equally effective when taken correctly, with a 9% chance of getting pregnant while using them.<\/span><\/p>"},{"question":4,"correctAnswer":0,"answerDescription":"<p><span style=\"background-color:transparent;color:rgb(0,0,0);\">Copper IUDs are known as a \u201cget it and forget it\u201d form of birth control for a reason. Once they\u2019re inserted, they can stay in place in your uterus for up to 10 years, with no need for any maintenance. Just remember that they should only be inserted and removed by a health care provider. And don\u2019t forget, this isn\u2019t a hormonal form of birth control; instead, that clever copper works to stop any sperm from moving through your uterus and finding (and then fertilizing) an egg. <\/span><\/p>"},{"question":6,"correctAnswer":2,"answerDescription":"<p><span style=\"background-color:transparent;color:rgb(0,0,0);\">Remember when we said earlier that some hormonal birth control options work by preventing ovulation? Well, nonhormonal forms of birth control, including cervical caps and diaphragms, won\u2019t affect ovulation. This means you will still ovulate and release an egg as usual during each menstrual cycle.<\/span><\/p>"},{"question":7,"correctAnswer":1,"answerDescription":"<p><span style=\"background-color:transparent;color:rgb(0,0,0);\">All types of IUDs can also be used as emergency contraception, if necessary. They\u2019re actually the most effective form of emergency contraception and can be almost 100% effective at preventing pregnancy if they\u2019re inserted within five days of having unprotected sex.<\/span><\/p>"},{"question":8,"correctAnswer":3,"answerDescription":"<p><span style=\"background-color:transparent;color:rgb(0,0,0);\">The withdrawal method, or pullout method, has a 22% chance of pregnancy. This method involves one partner removing their penis from the other partner\u2019s vagina before they ejaculate (or cum) to prevent sperm from entering the vagina and being able to fertilize an egg. This method is tricky to get right, and even when it\u2019s done perfectly, experts advise that it\u2019s still not 100% effective. Plus, don\u2019t forget that pre-ejaculate (or precum) can also contain sperm! Not to mention the fact that this method doesn\u2019t protect against STIs.<\/span><\/p>"},{"question":9,"correctAnswer":2,"answerDescription":"<p><span style=\"background-color:transparent;color:rgb(0,0,0);\">Your health care provider will usually inject the birth control shot into your upper thigh or arm. You might even be able to inject yourself at home if you opt for the lower-dose version of the shot, which contains less progestin. The birth control shot has just a 6% chance of pregnancy when the shots are taken at the right time, and each one can last for around 12 weeks.<\/span><\/p>"},{"question":10,"correctAnswer":1,"answerDescription":"<p><span style=\"background-color:transparent;color:rgb(0,0,0);\">If an external condom slips or breaks during sex, it\u2019s likely to be less effective at preventing pregnancy or protecting against STIs. If that happens and you\u2019re worried, it could be a good idea to take emergency contraception. Research suggests that external condoms slipping or breaking during sex is pretty rare, though. It\u2019s only thought to happen around 2% of the time. Phew!<\/span><\/p>"},{"question":11,"correctAnswer":0,"answerDescription":"<p><span style=\"background-color:transparent;color:rgb(0,0,0);\">If you decide to opt for an IUD, you\u2019ll need to speak to your health care provider for a prescription. Your doctor will do a pelvic exam before gently inserting the IUD into your uterus. This might feel a bit uncomfortable, and you could also experience some cramping just after it\u2019s inserted. If you have any questions or concerns, always speak to your doctor for advice.<\/span><\/p>"}]}
You scored:
Phew! When it comes to birth control, there’s a lot of information to take in, so hopefully this quiz has helped you make sense of all the options available.
If you want to learn even more about the different types of birth control methods available, as well as how they work and how effective they can be, you can find a whole range of informative articles here. And don’t forget that you can use an app like Flo to track any symptoms you may have or chat with other users about their experiences using birth control.
Next level of knowledge and insights
Accurate cycle predictions and knowledge of 100+ medical professionals at your disposal.
How Flo can help me?
With over 100+ medical experts, Flo supports women during their entire reproductive lives and provides curated cycle and ovulation tracking, personalized health insights, expert tips, and a fully closed community for women to share their questions and concerns.
Over 240 million people have downloaded Flo, and 48 million people use it on a monthly basis, which makes Flo the most popular women’s health app globally.
Well done! From condoms to cervical caps, you’re clearly an ace when it comes to knowledge about birth control.
If you want to learn even more about the different types of birth control methods available, as well as how they work and how effective they can be, you can find a whole range of informative articles here. And don’t forget that you can use an app like Flo to track any symptoms you may have or chat with other users about their experiences using birth control.
Next level of knowledge and insights
Accurate cycle predictions and knowledge of 100+ medical professionals at your disposal.
How Flo can help me?
With over 100+ medical experts, Flo supports women during their entire reproductive lives and provides curated cycle and ovulation tracking, personalized health insights, expert tips, and a fully closed community for women to share their questions and concerns.
Over 240 million people have downloaded Flo, and 48 million people use it on a monthly basis, which makes Flo the most popular women’s health app globally.