Candida overgrowth can result in many different symptoms that look different from the more commonly known vaginal yeast infection. Fatigue, gastrointestinal distress, and even chronic sinus infections can be signs of this sometimes stubborn condition. Still, there are many treatment options, and relief from candida is completely possible.
-
Tracking cycle
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Help Center
-
Flo for Partners
-
Anonymous Mode
-
Flo app reviews
-
Flo Premium New
-
Secret Chats New
-
Symptom Checker New
-
Your cycle
-
Health 360°
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Being a mom
-
LGBTQ+
-
Quizzes
-
Ovulation calculator
-
hCG calculator
-
Pregnancy test calculator
-
Menstrual cycle calculator
-
Period calculator
-
Implantation calculator
-
Pregnancy weeks to months calculator
-
Pregnancy due date calculator
-
IVF and FET due date calculator
-
Due date calculator by ultrasound
-
Medical Affairs
-
Science & Research
-
Pass It On Project New
-
Privacy Portal
-
Press Center
-
Flo Accuracy
-
Careers
-
Contact Us
How to Get Rid of Candida: 5 Dietary Changes to Consider


Every piece of content at Flo Health adheres to the highest editorial standards for language, style, and medical accuracy. To learn what we do to deliver the best health and lifestyle insights to you, check out our content review principles.
What is candida overgrowth?
Candida overgrowth is a very common condition. Often experienced as a vaginal yeast infection, with symptoms such as itchiness and a thick discharge, candida overgrowth can manifest itself in ways beyond the vaginal yeast infection and can affect men as well as women and children.
Candida yeast is one of the trillions of bacteria common to every single person. It can be found in the digestive tract, mouth, vagina, rectum, and on the skin. When within normal levels, it doesn’t bother us in any way. But if it grows, candida can become a health concern. Candida overgrowth is, in fact, the most common kind of fungal infection.
Common causes of candida
There are a number of reasons for candida overgrowth. The two most common factors are excessive antibiotic use and a high-sugar diet, but other factors can contribute to its growth as well.
While antibiotics help remove the bad bacteria that cause illness, they also remove the good bacteria living in our guts. If someone already has higher-than-normal levels of candida, a round of strong antibiotics can give them a candida fungal infection. Individuals with uncontrolled diabetes are also more likely to experience an overgrowth of candida. They may also find the condition harder to treat.
Even though the link is not entirely clear, a compromised immune system may be to blame. In fact, anyone who has a weakened immune system is more susceptible to developing a candida overgrowth. Another reason diabetics are more at risk of suffering from candida may be because the disease typically causes high blood sugar. Because sugar is candida’s main fuel source, blood sugar levels can play a part in causing a candida overgrowth.
There are a number of reasons for candida overgrowth. The two most common factors are excessive antibiotic use and a high-sugar diet.
Take a quiz
Find out what you can do with our Health Assistant
What about food and drink? Both can be triggers, under the right circumstances. A diet high in sugar and carbohydrate-rich foods can influence candida growth. Excessive alcohol intake can also be a culprit. This is because candida loves the sugar in alcohol.
In addition to certain conditions or drugs, high stress can trigger a candida overgrowth. It is less likely that stress alone causes an overgrowth, but it can certainly contribute to conditions that do. Chronic stress can also make treating candida more difficult. For these reasons, look for techniques for managing stress on a daily basis.
Symptoms of candidiasis
Candidiasis, the official name for candida overgrowth, has many more symptoms than the more familiar vaginal infection. The most common symptoms include:
- Recurring vaginal yeast infections — All women have candida living in their vaginal tracts, and up to 75 percent will experience a yeast infection at some point. But although they are common, having recurring yeast infections could be a sign that you have a candida fungal infection. Symptoms of yeast infection typically include intense itchiness and a thick discharge. Although mostly seen in people who are elderly or immunocompromised, reoccurring urinary tract infections (UTIs) can also be caused by candida overgrowth. UTI symptoms include a burning sensation when urinating and pressure or pain in the lower abdomen.
- Digestive issues — Signs of gastrointestinal distress, such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, constipation, and cramps, can be caused by candida. Candida overgrowth is also associated with certain diseases of the digestive tract like Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
- Chronic sinus infections — Sinus infections are common, infecting one in eight people yearly. Typically caused by bacteria, chronic sinus infections that do not go away may be caused by a fungal infection. Symptoms include headaches, nasal congestion, runny nose, and a loss of smell. For acute conditions, antibiotics may help, but if the condition is chronic, antibiotics may worsen symptoms, particularly if the culprit is candida.
- Fatigue and tiredness/chronic fatigue syndrome — If you are immunocompromised, you may be feeling more fatigued or tired. But a compromised immune system also leaves you more susceptible to candidiasis. Many who have candida overgrowth also report feeling tired. Candidiasis may also be a root cause of chronic fatigue syndrome, a condition characterized by extreme feelings of fatigue. Other symptoms include loss of memory or concentration, headaches, and an ongoing feeling of complete exhaustion.
Candida overgrowth treatment options
If you are experiencing some of these symptoms, you may be wondering how to get rid of candida. Fortunately, there are a number of treatment options available. From changes in diet and lifestyle to taking certain fungicides, it is possible to stop candida overgrowth and return your body to a state of balance.
Eliminate your sugar intake
Because sugar is candida’s primary source of fuel, the best place to begin is to stop any obvious (and not-so-obvious) sugar intake. Remember that sugar can hide in places like yogurt and granola bars. To really tackle candida head on, avoid all foods that contain sugar as an ingredient, even if it isn’t the first on the ingredient list.
Cut down on carbs
Although carbs may not contain sugar per se, once eaten, they turn into sugar. For this reason, it is better to avoid them, or at least cut down on carbs, during a candida cleanse, particularly from refined sources like breads, crackers, and chips. Some carbs such as rice have an even greater glycemic load than certain sweeteners such as honey.
Stay away from high-lactose dairy products
Dairy is similar to carbs. Once ingested, it breaks down into sugar. Dairy is also considered an inflammatory food that can further irritate an already leaky gut caused by an overgrowth of candida.
Go for gluten-free products
In addition to being highly inflammatory, gluten can be part of a vicious cycle for those suffering from candidiasis. There is some evidence that candida may be a root cause for those with a non-celiac gluten sensitivity. If you fall into this category, you have all the more reason to want to heal your candida. Doing so may mean you will be able to tolerate gluten again. In any case, better sources of carbs during a candida cleanse are starchy veggies and some high-protein, gluten-free grains such as amaranth and quinoa. Thankfully, there are a number of gluten-free fast-food options available.
Reduce alcohol intake
When alcohol breaks down in your body, it essentially continues feeding candida. Fermented alcohol in particular, including beer and wine, has higher amounts of sugar and gluten, both of which are inflammatory.
How long does it take to get rid of candida?
How long it takes to get rid of candida depends on several factors. For some, a single round of antifungal treatment will be enough to do the trick. Others, particularly those with compromised immune systems, may find it takes longer to kick candida completely. Diet and lifestyle changes, such as eliminating inflammatory foods like processed products and sugars, can go a long way towards keeping candida gone for good.

Track symptoms and patterns
Learn to spot patterns in your cycle as they can provide insight into underlying medical conditions
When to seek medical help
If you are struggling and unsure how to get rid of candida overgrowth, consider seeking medical help. If you have symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome, Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, or are immunocompromised, speak with your doctor. Breastfeeding mothers whose babies have thrush should also speak with their ob-gyns. Your doctor may want to prescribe antifungal medications.
The takeaway
When it comes to candida overgrowth, prevention is key. In other words, eating healthy, avoiding processed and sugary foods and alcohol, and managing stress levels will go a long way toward keeping candida from getting out of control. Still, relief is possible. If you are suffering, a combination of diet, lifestyle, and antifungal medications can effectively stop candida for good.
Hey, I'm Anique
I started using Flo app to track my period and ovulation because we wanted to have a baby.
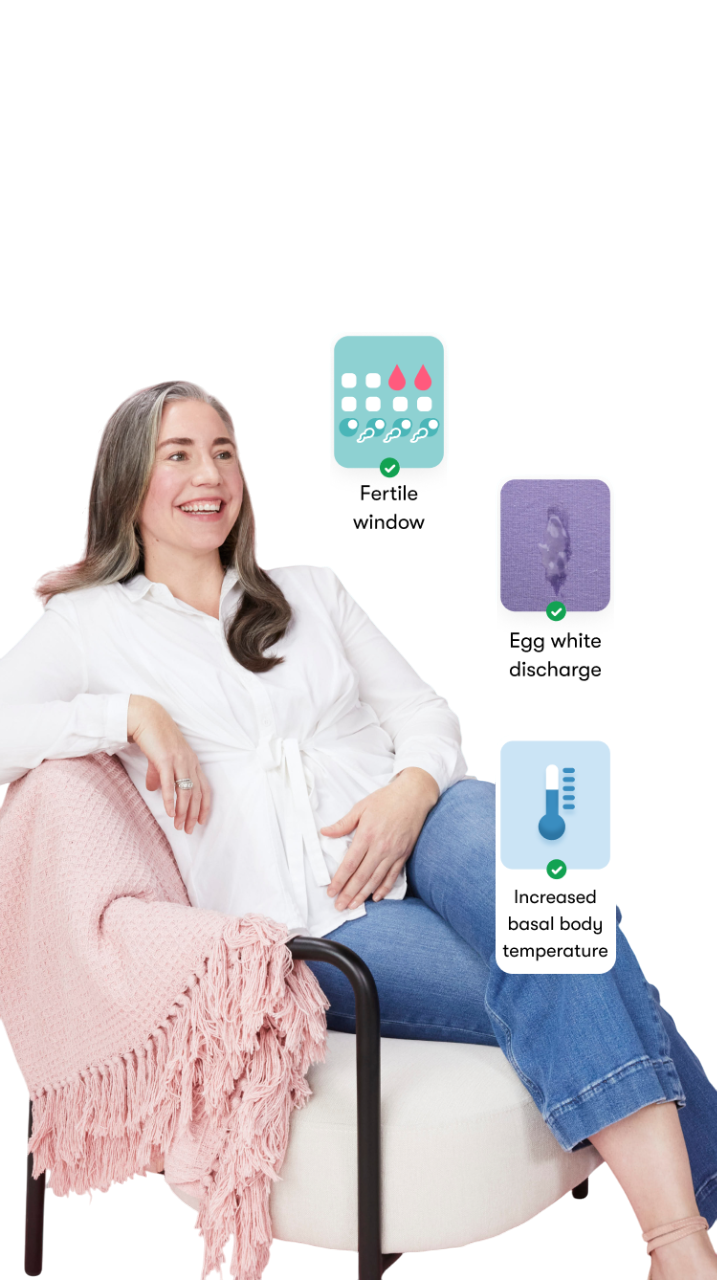

The Flo app helped me learn about my body and spot ovulation signs during our conception journey.
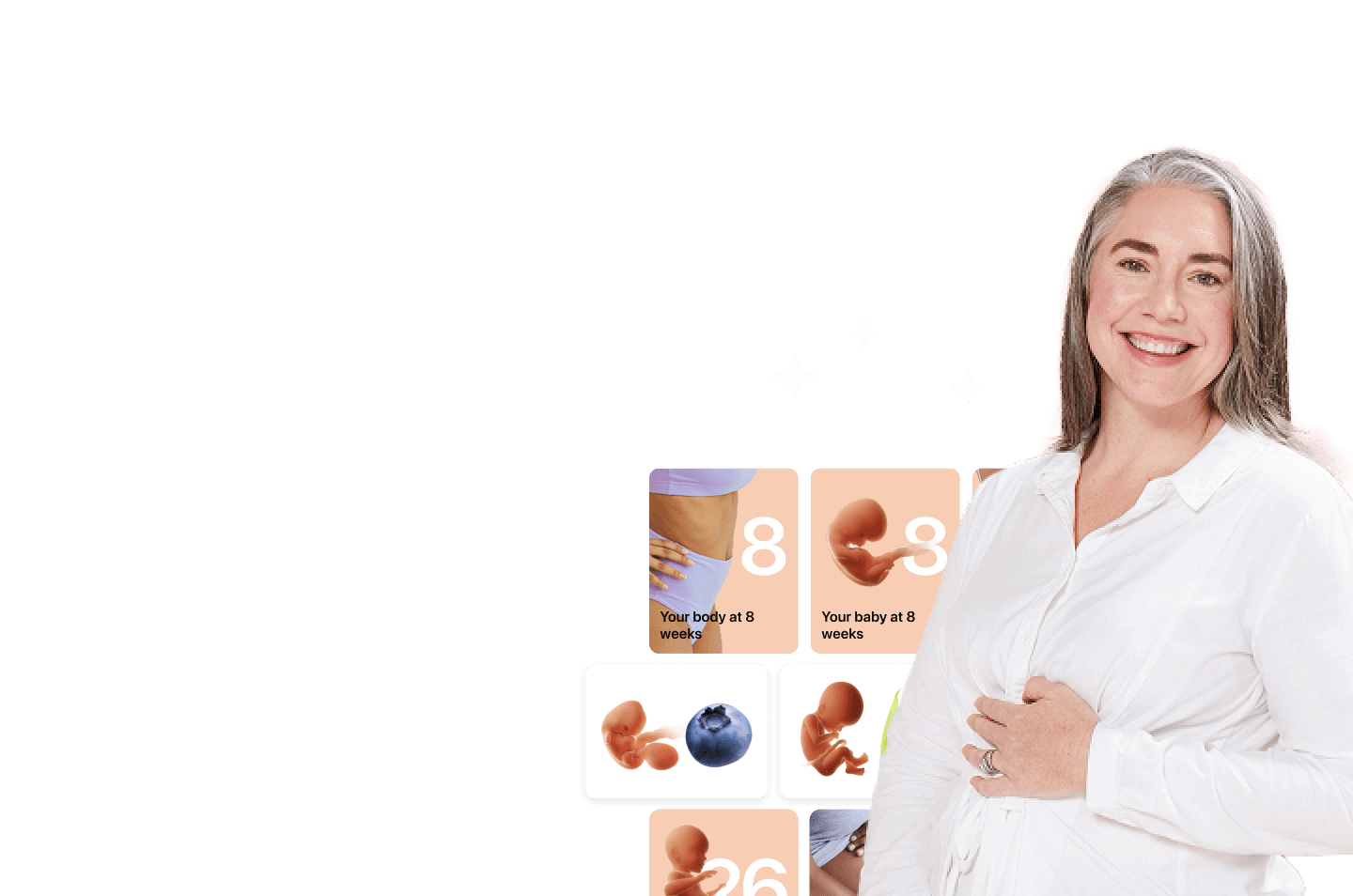
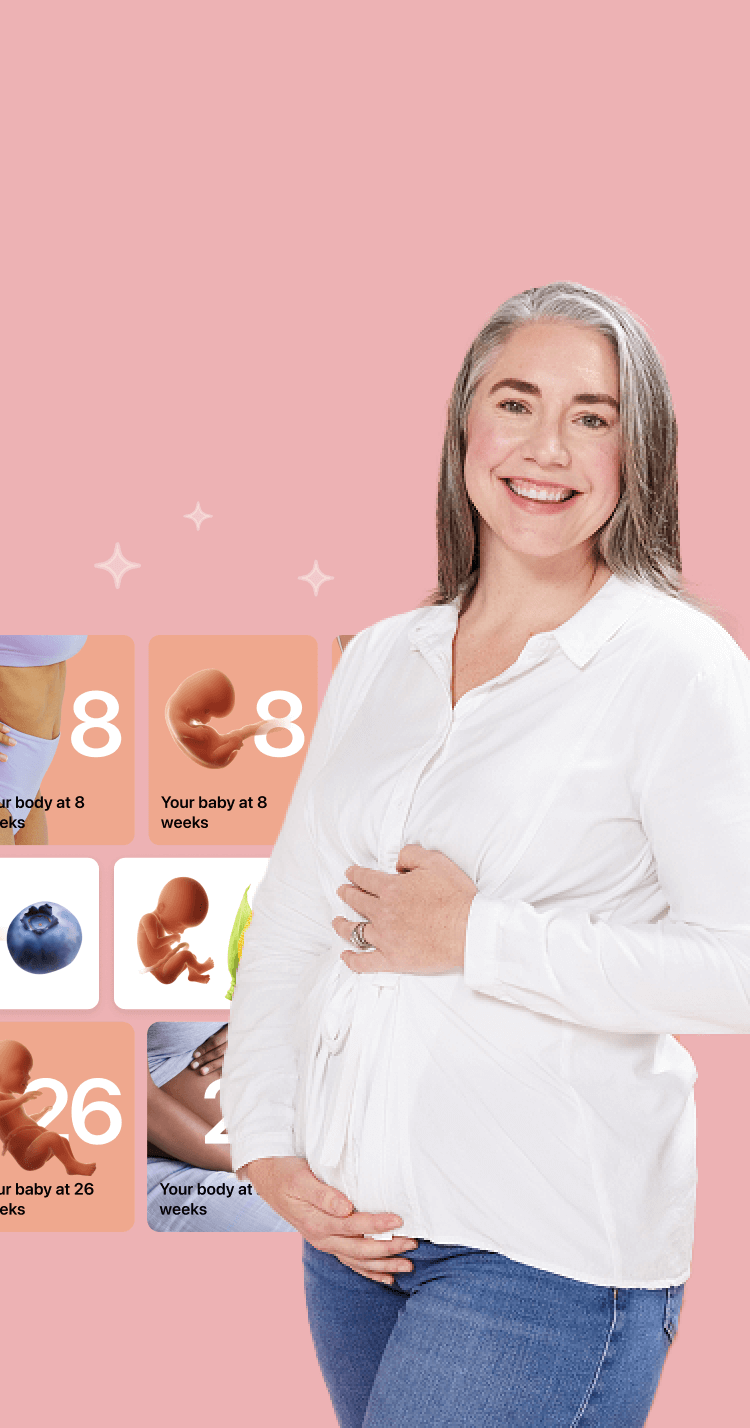


I vividly
remember the day
that we switched
Flo into
Pregnancy Mode — it was
such a special
moment.
Real stories, real results
Learn how the Flo app became an amazing cheerleader for us on our conception journey.




