Gender and gender identity are nuanced, complex topics that might not be totally intuitive for everyone. If you’re interested in learning more about them, whether you’re exploring your own gender identity or you’d like to know how to support trans and nonbinary people in your community, keep reading. We’ve asked Kathryn Macapagal from the Institute for Sexual and Gender Minority Health and Wellbeing to shed some light on the issue and answer eight of the most common questions about sex and gender identity.
-
Tracking cycle
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Help Center
-
Flo for Partners
-
Anonymous Mode
-
Flo app reviews
-
Flo Premium New
-
Secret Chats New
-
Symptom Checker New
-
Your cycle
-
Health 360°
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Being a mom
-
LGBTQ+
-
Quizzes
-
Ovulation calculator
-
hCG calculator
-
Pregnancy test calculator
-
Menstrual cycle calculator
-
Period calculator
-
Implantation calculator
-
Pregnancy weeks to months calculator
-
Pregnancy due date calculator
-
IVF and FET due date calculator
-
Due date calculator by ultrasound
-
Medical Affairs
-
Science & Research
-
Pass It On Project New
-
Privacy Portal
-
Press Center
-
Flo Accuracy
-
Careers
-
Contact Us
Sex, Gender, and Gender Identity — 8 Questions Answered by an Expert


Every piece of content at Flo Health adheres to the highest editorial standards for language, style, and medical accuracy. To learn what we do to deliver the best health and lifestyle insights to you, check out our content review principles.
Sexual orientation and gender identity: What's the difference?
Sexual orientation consists of different dimensions. Although there are different models of sexual orientation, current research suggests that there might be at least three different aspects to sexual orientation, which are:
- Who you are attracted to sexually
- The type(s) of people that you have sex with
- The sexual orientation identity label that you identify with
These aspects of sexual orientation don't always line up with each other. Sometimes they do; sometimes they don't. And that's all okay.
For example, if you identify as heterosexual, or straight, you might only have sex with and be attracted to people who are of a different sex or gender than you. But that's not always the case. Other folks who identify as heterosexual might be attracted to and have had sexual experiences with people of all genders but are predominantly attracted to one gender.
Gender identity is how you experience gender on the inside, whether you feel more masculine, feminine, both, or neither. Your gender identity might be the same as the sex that you were given at birth, or it might be different. For example, if you identify as a woman and you were assigned female at birth, we call that being a cisgender woman.
Cisgender means that your gender identity and your birth sex are the same. Other folks might identify as a woman but were assigned male at birth, in which case, they are transgender women.
Transgender means that your gender identity and birth sex are different from each other.
What kinds of gender identities exist?
Our understanding of gender identity and the language around gender has changed a lot in recent years.
People have more fine-grained labels for their identity. For the most part, you can classify gender identities as masculine, feminine, both, something in between, or neither.
Many people identify as cisgender women, cisgender men, transgender women, and transgender men. More and more people are identifying as genderqueer or non-binary, meaning that they don't identify with either masculine or feminine gender identities or subscribe to binary gender identities.
What is bigender?
"Bi" means two or more, or double. Somebody who is bigender might experience two gender identities at the same time or go back and forth between the two. It could be that you have a sense of being male and female, or female and nonbinary, or male and nonbinary, for example.
What is genderqueer?
Genderqueer is a gender identity label used when people identify as more than one gender, neither gender, or both genders, or more than one gender. It also might be used when a person doesn't subscribe to or adhere to binary male/female gender stereotypes or distinctions.
Do people choose their sexual orientation and gender identity?
You can't choose who you're attracted to or what gender you feel on the inside. People certainly can decide who they want to have sex with. They can choose what specific sexual orientation labels and gender identity labels they want to use and how they want to express their gender on the outside, like through their clothes or their mannerisms.
That said, how people experience their sexuality or gender and what labels fit them might vary over time as they learn more about themselves and different terms to describe their sexuality and gender.
For instance, a person who’s identified as heterosexual their whole life might come to realize later in life they have been attracted to people of more than one gender but didn’t have the words or label to describe their experience before.
Can people change their sexual orientation and gender identity?
It is not possible to change who you are attracted to or the gender you feel inside. Unfortunately, there are a lot of conversion therapies that attempt to change people's sexual orientation to be heterosexual and gender identity to be cisgender. It is very harmful medically and psychologically for a person to be exposed to conversion therapy or other efforts to try to change their sexual orientation or gender identity.
If people are struggling with their sexual orientation and gender identity, it’s better to find a therapist or health care provider who is affirming and supportive of their sexuality and gender, whatever it may be.
What can help people understand their sexual orientation and gender identity?
Sometimes, people know from a very young age that they are attracted to people of the same sex or gender, or that their gender identity, or their gender that they feel on the inside, is different from what society feels like it should be.
There are people who know that very early or that their sexual orientation or gender identity are different somehow. But that's not always the case. People might come to understand their sexual orientation and gender identity later on in life.
There are a variety of things that can help people get a better sense of their sexual orientation or gender identity. One major thing is exposure to role models -- for example, to people with different sexual orientations and gender identities and media that feature people of different sexual orientations and gender identities.
Similarly, information on the internet and getting connected with LGBTQ communities online can help people get the language and terms they need to better describe and make sense of how they feel on the inside.
How can people express their gender identity?
People can express their gender identity through gender presentation, which is how they express their gender through hairstyles, dress, their voice, and the way they carry themselves and move their bodies.
People can also express their gender identity by talking about their gender identity, of course.
Take a quiz
Find out what you can do with our Health Assistant
Hey, I'm Anique
I started using Flo app to track my period and ovulation because we wanted to have a baby.
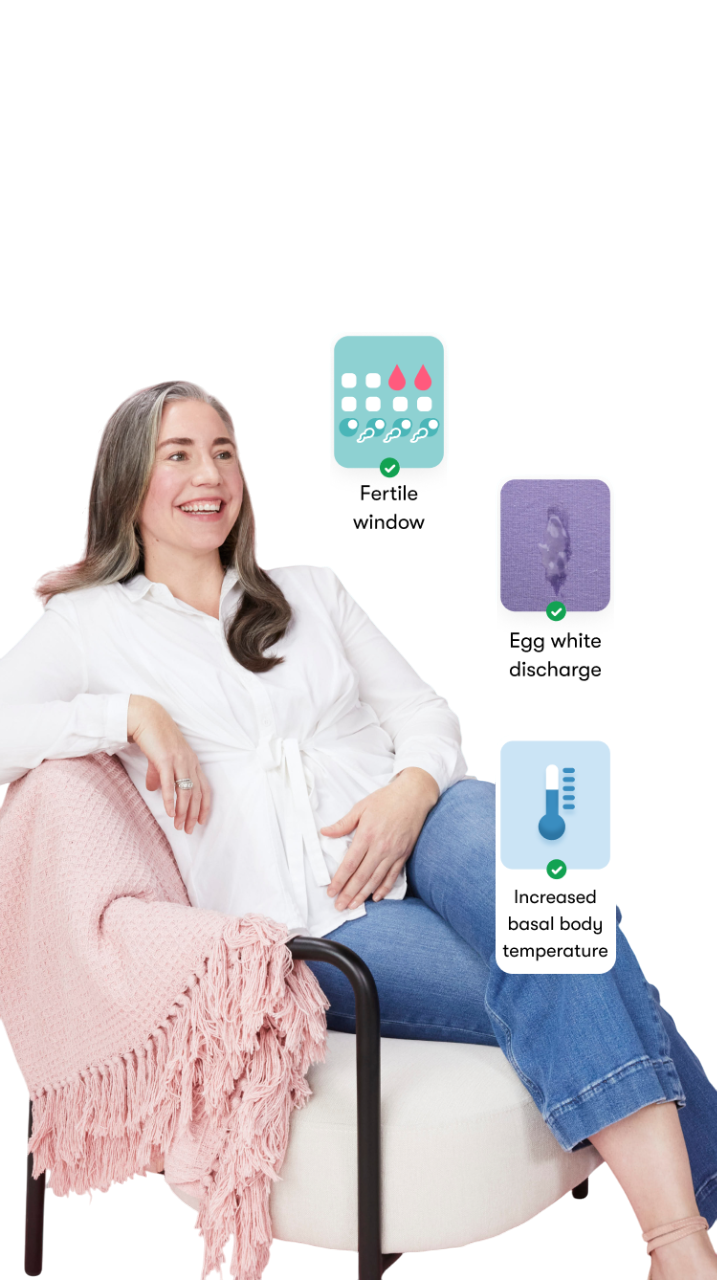

The Flo app helped me learn about my body and spot ovulation signs during our conception journey.


I vividly
remember the day
that we switched
Flo into
Pregnancy Mode — it was
such a special
moment.
Real stories, real results
Learn how the Flo app became an amazing cheerleader for us on our conception journey.




