-
Tracking cycle
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Help Center
-
Flo for Partners
-
Anonymous Mode
-
Flo app reviews
-
Flo Premium New
-
Secret Chats New
-
Symptom Checker New
-
Your cycle
-
Health 360°
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Being a mom
-
LGBTQ+
-
Quizzes
-
Ovulation calculator
-
hCG calculator
-
Pregnancy test calculator
-
Menstrual cycle calculator
-
Period calculator
-
Implantation calculator
-
Pregnancy weeks to months calculator
-
Pregnancy due date calculator
-
IVF and FET due date calculator
-
Due date calculator by ultrasound
-
Medical Affairs
-
Science & Research
-
Pass It On Project New
-
Privacy Portal
-
Press Center
-
Flo Accuracy
-
Careers
-
Contact Us
Ankyloglossia or Tongue Tie: Definition, Symptoms, and Complications


Every piece of content at Flo Health adheres to the highest editorial standards for language, style, and medical accuracy. To learn what we do to deliver the best health and lifestyle insights to you, check out our content review principles.
What is ankyloglossia?
The tongue is a strong and flexible muscle, and it must be able to move in various directions to manipulate food and allow for the enunciation of certain sounds. It's the length of the tongue web, also known as the lingual frenulum, that controls this flexibility.
Some babies are born with a lingual frenulum that is shorter than normal. This limits the extent to which the tongue can be flexible, sometimes preventing it from extending past the lower line of teeth.
The free tongue refers to the length of the tongue from the tip to the base where the lingual frenulum connects with it. Normally, the free tongue is longer than 16 millimeters (mm). The degree to which the free tongue is shorter than this helps identify the extent of a baby's ankyloglossia.
- Class I is when the free tongue is between 12 and 16 mm long
- Class II is between 8 and 11 mm
- Classes III and IV are more severe, referring to cases where the free tongue is between 3 and 7 mm or less than 3 mm long, respectively
Does tongue tie affect breastfeeding?
For your baby to breastfeed, he or she must be able to latch onto the nipple. In order to latch on properly, the tongue needs to extend forward and cover the lower gum. This makes feeding comfortable for you.
When the baby is tongue-tied, the range of motion of tongue is limited and he or she cannot sufficiently extend the tongue. This prevents the baby from getting the tongue over the lower lip and gum ridge and can cause feeding problems, particularly affecting breastfeeding.
Mothers of babies with tongue tie can experience pain when the baby clamps down on the nipple — enough to make you want to stop breastfeeding. In some cases, adjusting to find a more ideal position to breastfeed can help relieve some of this pain.
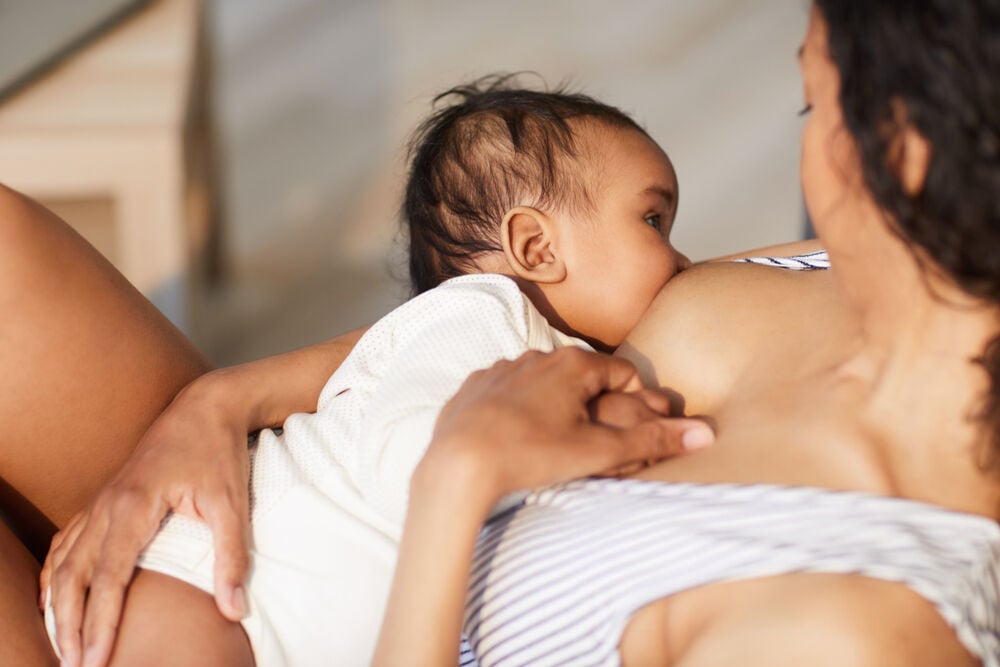

If your baby has a short tongue web, you might notice that he or she:
- Has difficulty latching onto the nipple
- Latches for only a short time
- Makes a clicking sound when suckling, indicating that the latch is incorrect
- Is fussy and seems hungry most of the time
- Doesn’t gain weight
It's not difficult to see how ankyloglossia can deny the baby many of the benefits of breastfeeding. What else can it affect?
Take a quiz
Find out what you can do with our Health Assistant
Will ankyloglossia cause speech problems?
The tongue is an essential component in speech. For you to be able to pronounce words, you need the full range of motion of your tongue to enunciate different syllables.
With reduced mobility of the tongue, the articulation of sounds varies from the correct enunciation. There are some sounds that can only be articulated using tongue movement at the front of the mouth, and any slight deviation in such phonetics is easy to notice. Other sounds require more vibration and, there is therefore compensation along the other areas of the sound articulation system.
The most commonly mispronounced consonants and sounds due to tongue tie are s, z, t, d, l, j, zh, ch, th, and dg.
Other tongue-tie complications
When your baby is tongue-tied, he or she will likely to encounter other complications further down the road. These include:
- Inefficient manipulation of solid food
- Impaired mobility of the tongue to sweep back bits of food, leading to gingivitis and tooth decay
- Difficulty licking, making your child dread and shun some foods
- Chapped lips due to the inability to properly lick lips
- Development of a gap between the lower incisors
Later on in life, your child might find it difficult to play a wind musical instrument. During adolescence, kissing can also become challenging due to the limited range of tongue motion.
Do babies with ankyloglossia need treatment?
Earlier on, we discussed the different classes of ankyloglossia. Class I is a mild form of the condition that your baby might be able to live with, without any considerable interference in his or her normal lifestyle.
However, as you progress further down the scale, classes III and IV provide extremely limited motion of the tongue. In these severe cases, it's important for your baby to receive ankyloglossia treatment in order to be able to breastfeed and learn to speak.
Early treatment is also recommended for the moderate class II to ensure that the baby will have no difficulty eating and speaking in the future.
Tongue-tie: surgery procedure for babies
If you notice that your newborn has tongue tie, talk to your doctor about finding a solution for your little one.
Surgery is usually the best way to go. Ankyloglossia surgery is generally quick and painless, often taking place right in the doctor’s office. With a sterile pair of scissors, the doctor snips the lingual frenulum away, freeing the tongue to move more. This procedure — known as frenotomy — has little or no bleeding because the tongue web isn’t well supplied with blood or nerves.
If extensive repair is needed, or if the baby has a thick lingual frenulum, the doctor may perform the procedure under general anesthesia with stitches afterward. This procedure is known as frenuloplasty. The doctor will also recommend tongue exercises to reduce scarring and help promote a greater range of movement.
In a nutshell, ankyloglossia is a condition where your baby's tongue has limited movement because he or she has a short lingual frenulum. This brings about complications during breastfeeding and in speech, but it can be easily treated through surgery.
Hey, I'm Anique
I started using Flo app to track my period and ovulation because we wanted to have a baby.

The Flo app helped me learn about my body and spot ovulation signs during our conception journey.


I vividly
remember the day
that we switched
Flo into
Pregnancy Mode — it was
such a special
moment.
Real stories, real results
Learn how the Flo app became an amazing cheerleader for us on our conception journey.




