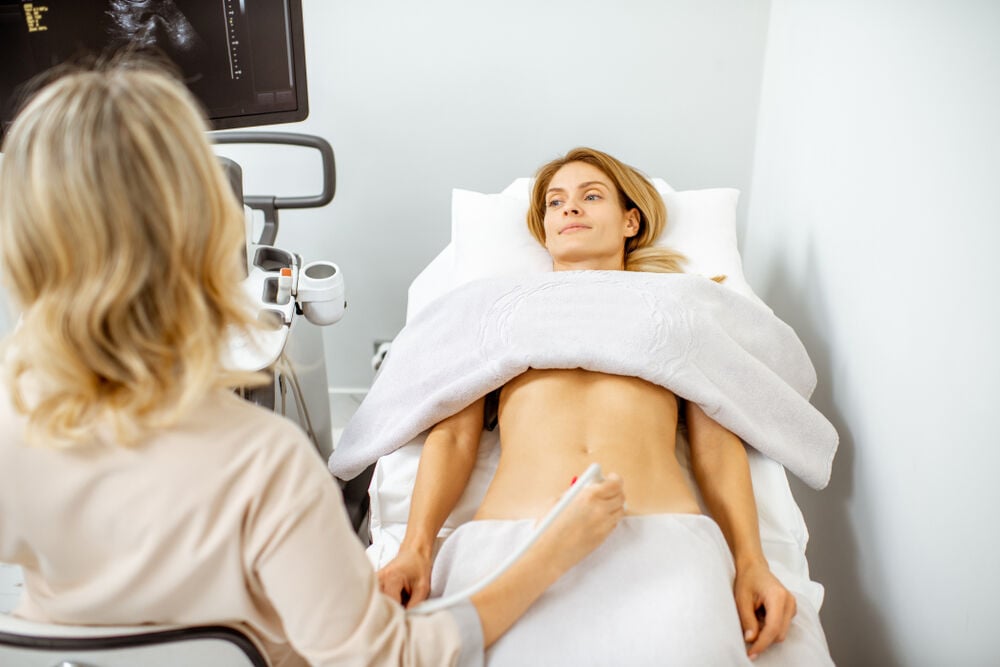
Having an enlarged ovary can be alarming. Depending on your age and menstrual cycle, however, it can be quite normal to have swollen ovaries from time to time.
The size of ovaries changes throughout the cycle. There are also several reasons you may have swollen ovaries. If you’re wondering if you have enlarged ovaries or about the possible causes of your swollen ovaries, then read on. We’ve listed common causes of an enlarged ovary, as well as ways to diagnose and treat it if needed.