Vaginal folliculitis, or genital folliculitis, is very common and can occur on and off throughout your lifetime. Folliculitis looks like acne in the genital region. The main difference is that acne is a clogged or infected pore, while a folliculitis bump is actually an infected hair follicle. You can spot the difference between the two by identifying a hair in the middle of a folliculitis bump.
-
Tracking cycle
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Help Center
-
Flo for Partners
-
Anonymous Mode
-
Flo app reviews
-
Flo Premium New
-
Secret Chats New
-
Symptom Checker New
-
Your cycle
-
Health 360°
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Being a mom
-
LGBTQ+
-
Quizzes
-
Ovulation calculator
-
hCG calculator
-
Pregnancy test calculator
-
Menstrual cycle calculator
-
Period calculator
-
Implantation calculator
-
Pregnancy weeks to months calculator
-
Pregnancy due date calculator
-
IVF and FET due date calculator
-
Due date calculator by ultrasound
-
Medical Affairs
-
Science & Research
-
Pass It On Project New
-
Privacy Portal
-
Press Center
-
Flo Accuracy
-
Careers
-
Contact Us
Vaginal Folliculitis and Treatment Options


Every piece of content at Flo Health adheres to the highest editorial standards for language, style, and medical accuracy. To learn what we do to deliver the best health and lifestyle insights to you, check out our content review principles.
Although genital folliculitis may be a bit painful, you can easily prevent it and treat it at home. Without prompt attention, however, an infected follicle can develop into a genital abscess, which will need medical attention.
What causes genital folliculitis?
Folliculitis, even in the genital region, is generally not contagious. However, due to the proximity of hair follicles to one another in the vaginal region, the infection can spread from one to the next, eventually looking like a patch of acne.
Folliculitis happens when your hair follicles are damaged. When they’re damaged, it’s easy for germs to get inside the follicles and cause an infection. The infection can be caused by bacteria, usually by Staphylococcus aureus (staph), viruses, or fungi.
Hair follicles can be damaged by:
- Touching or rubbing your skin frequently
- Wearing tight clothing
- Shaving
The initially infected follicle may occur as a result of an ingrown hair, caused by a follicle blocked by sweat and dead skin cells. Genital folliculitis is more common in areas of the body where hair is rough and often shaved, including the vaginal region. There, the hair is coarser, the skin is more sensitive, and the risk of bacterial infection from razors or other hair removal products is higher.
The skin around the vagina and inner thighs is thinner and more sensitive than the skin on other parts of the body. Tight clothing and elastic underwear bands can cause excess friction; that, coupled with sweat from vigorous exercise or even just continuous walking creates an environment that is ideal for folliculitis to occur. Tight clothing can slough off dead skin cells, and then sweat and oils in that area become trapped in the hair follicles. Skin is especially susceptible after shaving.
Dirty hot tubs and spas can also cause folliculitis, as bacteria thrive in inadequately chlorinated warm water. Make sure to clean in between your legs and around your vagina thoroughly after sex and after using a hot tub to reduce your chances of infected hair follicles. You may also experience higher occurrences of vulvar folliculitis during your period due to the shifts in hormone levels.
Main types of vulvar folliculitis
Irritant folliculitis. Redness, chafed skin, and itchiness is commonly referred to as “razor burn” and occurs within 36 hours of shaving. The injured follicles are highly susceptible to becoming infected. The sensitive skin of the inner thighs and vaginal region is especially susceptible to irritation, for example, from tight clothing against the skin or from a partner who has recently shaved. To clear your skin more quickly and get relief, you can try applying warm compresses to the area. You can also try to relieve itchy skin with a soothing lotion.
Razor bumps (pseudofolliculitis barbae). Razor bumps are the result of an inflammatory reaction surrounding ingrown hairs. They can occur on any part of your body where hair is shaved. New hairs that grow back after removal may become trapped beneath the top layer of skin and curl backward. As the hair grows, the layers of your skin become irritated and can become infected. You can remove ingrown hairs with sterilized tweezers or seek a professional dermatologist or aesthetician certified in genital hair removal.
Hot tub folliculitis (pseudomonas folliculitis). This shows up as a rash of red, round, itchy bumps. Hot tub folliculitis is caused by pseudomonas bacteria, which can be found in hot tubs and heated pools where the chlorine and pH levels are out of balance.
Take a quiz
Find out what you can do with our Health Assistant
Warm compresses used in vaginal folliculitis treatment

Explore more about sexual health
Genital folliculitis symptoms
Vaginal folliculitis looks like a pimple on the inner thighs, labia, or pubic mound area. You can tell the difference between an acne pimple and vaginal folliculitis by looking for a hair. If there’s a hair in the middle of the bump, it’s genital folliculitis or an infected hair follicle. If there’s no hair in the middle, then it’s probably vaginal acne. If you aren’t sure, visit your OB-GYN or dermatologist for a diagnosis.
Folliculitis, unlike genital acne, is typically painless, although the bumps may be red or sore. There are also sometimes symptoms of infection associated with folliculitis such as itching, crusty sores, and low fever. Folliculitis looks like a mosquito bite or raised bump. Vaginal folliculitis caused by ingrown hairs may look like a small splinter under the skin or a raised bump with a dark spot or line (this is the trapped hair).

Side effects of vaginal folliculitis
If left untreated, folliculitis can sometimes grow into boils or carbuncles. These are larger infections under the skin, full of pus, that can turn into abscesses. The risk of infection is higher the larger the boil is, and they should be treated in a sterile medical setting. While these may heal on their own, people with a compromised immune system may end up with a severe infection.
Permanent hair loss is a rare side effect. It occurs when the infection penetrates deep enough into the skin and damages the hair follicle, preventing regrowth.
Genital folliculitis treatment

Treatment for folliculitis includes medications and, in some cases, laser hair removal. Even if it helps, the infection may come back.
You need to be careful about treating folliculitis in the vaginal region to prevent transferring the infection and scarring. You can treat mild cases involving just a few infected hair follicles by using a warm compress to loosen the infection and allowing the skin to heal. If the infection was caused by shaving, plucking, or waxing, it’s best to skip those treatments for 30 days.
Medications for genital folliculitis
- Creams or pills to control infection — Your health care provider may prescribe an antibiotic cream for mild cases. Oral antibiotics may be prescribed for a severe or recurrent infection.
- Creams, shampoos, or pills for fungal infections — Antifungals are for infections caused by yeast rather than bacteria. Antibiotics aren’t helpful in treating this type of infection.
- Minor surgery — If you have a large boil or carbuncle, your health care provider may make a small incision in it to drain the pus to relieve pain and speed recovery.
- Laser hair removal — This method permanently removes hair follicles in the treated area. There are possible side effects, such as blistering and scarring.

Discover why you don’t need special cleaning products for your genitals
Preventing genital folliculitis
Preventing infected hair follicles in the pubic region includes practicing proper hygiene, including regular washing with warm water. Do not share towels, and change your washcloth often to prevent bacteria buildup.
It’s especially important to practice good vaginal hygiene during your period. Not only do hormonal shifts cause the skin to be more sensitive, but there’s also a higher population of bacteria that can infect hair follicles and chafed skin.
Use an exfoliant recommended by your dermatologist. Do not use facial products on your vulva unless prescribed. If you choose to shave, use a sharp, clean razor and change it frequently, or switch to an electric razor. Shave in the direction of the follicle, not against it. Make sure not to stretch the skin.
You can also consider alternative hair removal methods such as waxing, depilatories, or laser hair removal. These procedures remove the entire hair from the root. When the hairs grow back, they’re typically finer, with a smooth tip instead of the blunt, rough tip that shaved hairs have, reducing instances of ingrown hairs.
Genital folliculitis is generally mild and easily preventable with proper hygiene and care. However, it’s important to note that certain sexually transmitted infections (STIs) can look very similar to a folliculitis bump or vaginal acne. If you’re sexually active, make sure to get tested for STIs to be safe.
Hey, I'm Anique
I started using Flo app to track my period and ovulation because we wanted to have a baby.
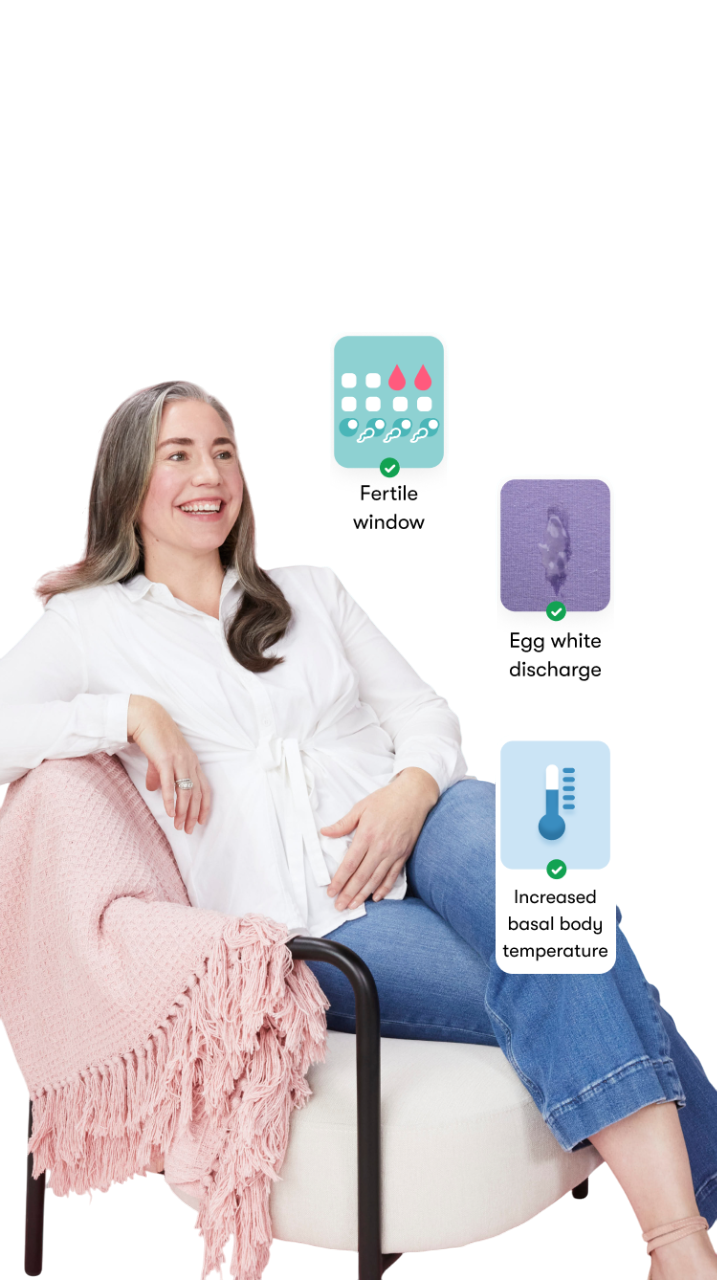

The Flo app helped me learn about my body and spot ovulation signs during our conception journey.


I vividly
remember the day
that we switched
Flo into
Pregnancy Mode — it was
such a special
moment.
Real stories, real results
Learn how the Flo app became an amazing cheerleader for us on our conception journey.
References
Margesson, Lynette J, and Hope K Haefner. “Vulvar Lesions: Differential Diagnosis Based on Morphology.” UpToDate, 2019, www.uptodate.com/contents/vulvar-lesions-differential-diagnosis-based-on-morphology.
“Acne-like Breakouts Could Be Folliculitis.” American Academy of Dermatology, www.aad.org/public/diseases/a-z/folliculitis.
“Folliculitis.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 8 Mar. 2018, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/folliculitis/symptoms-causes/syc-20361634.
Oakley, Amanda, and Clare Morrison. “Folliculitis.” Folliculitis | DermNet NZ, Apr. 2014, dermnetnz.org/topics/folliculitis/.
Oakley, Amanda. “Folliculitis Barbae and Pseudofolliculitis Barbae.” Folliculitis Barbae and Pseudofolliculitis Barbae | DermNet NZ, 1998, dermnetnz.org/topics/folliculitis-barbae/.
“Folliculitis.” Mayo Clinic, Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, 18 Aug. 2020, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/folliculitis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20361662.




