From pink to red, scarlet, and brown, there are lots of ways you can describe your period. But why does it change color?
-
Tracking cycle
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Help Center
-
Flo for Partners
-
Anonymous Mode
-
Flo app reviews
-
Flo Premium New
-
Secret Chats New
-
Symptom Checker New
-
Your cycle
-
Health 360°
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Being a mom
-
LGBTQ+
-
Quizzes
-
Ovulation calculator
-
hCG calculator
-
Pregnancy test calculator
-
Menstrual cycle calculator
-
Period calculator
-
Implantation calculator
-
Pregnancy weeks to months calculator
-
Pregnancy due date calculator
-
IVF and FET due date calculator
-
Due date calculator by ultrasound
-
Medical Affairs
-
Science & Research
-
Pass It On Project New
-
Privacy Portal
-
Press Center
-
Flo Accuracy
-
Careers
-
Contact Us
Period blood color chart: What you need to know


Every piece of content at Flo Health adheres to the highest editorial standards for language, style, and medical accuracy. To learn what we do to deliver the best health and lifestyle insights to you, check out our content review principles.
Ever seen your period blood in a pad or your underwear and thought, ”Wait … is that normal?” You’re not alone. The color of your menstrual blood can range from pink and bright red to deep brown. These color changes actually serve a pretty interesting purpose. They can be a good indicator of where you are in your cycle and your overall health.
Most of the time, period blood color changes are normal and just a reflection of how fast (or slow) your flow is. However, some color changes may indicate that something isn’t quite right. Knowing what’s typical for you may help you spot when it’s time to call your doctor.
So, here’s the lowdown on period blood color, from why it changes color to a handy color chart you can match yours against.
Key takeaways about period blood color
- The average period length is between two and seven days. If you notice that your period blood color changes during that time, fear not. This is totally typical and generally nothing to worry about.
- Period blood color can help you figure out at what point in your period you are, plus how fast or slow your flow is. Generally speaking, the faster your flow, the brighter red your period blood. This is because your period blood darkens the longer it’s outside your blood cells, as it reacts to oxygen.
- Alongside your period, your body also produces discharge throughout your cycle. This can also change color (and consistency) as your hormones fluctuate. However, some discharge colors (such as green) could indicate that you have an infection.
Take a quiz
Find out what you can do with our Health Assistant
Why does period blood change color?
When we think of blood, it’s normally bright berry red, and your period is no exception to this. However, if you look in your underwear and see something a little different, it isn’t necessarily anything to worry about.
It’s very typical for your period to appear red, pink, or even brown at different points. It’s a pretty good indicator of where you are in your cycle. Generally speaking, fresh blood that has just left your blood vessels is a bright, vivid red. This indicates that the blood is new and flowing pretty quickly. However, the longer that blood is out of your blood vessels, the longer it has to react with oxygen, turning it more of a brown color. This is known as oxidation.
Think about it: If you’ve ever fallen and grazed your knee, the blood that immediately appears will likely be bright red before drying and turning brown. And this logic can apply to your period as well.
The period blood color chart
How bright your period blood is can indicate how fast your flow is and where you are in your cycle.
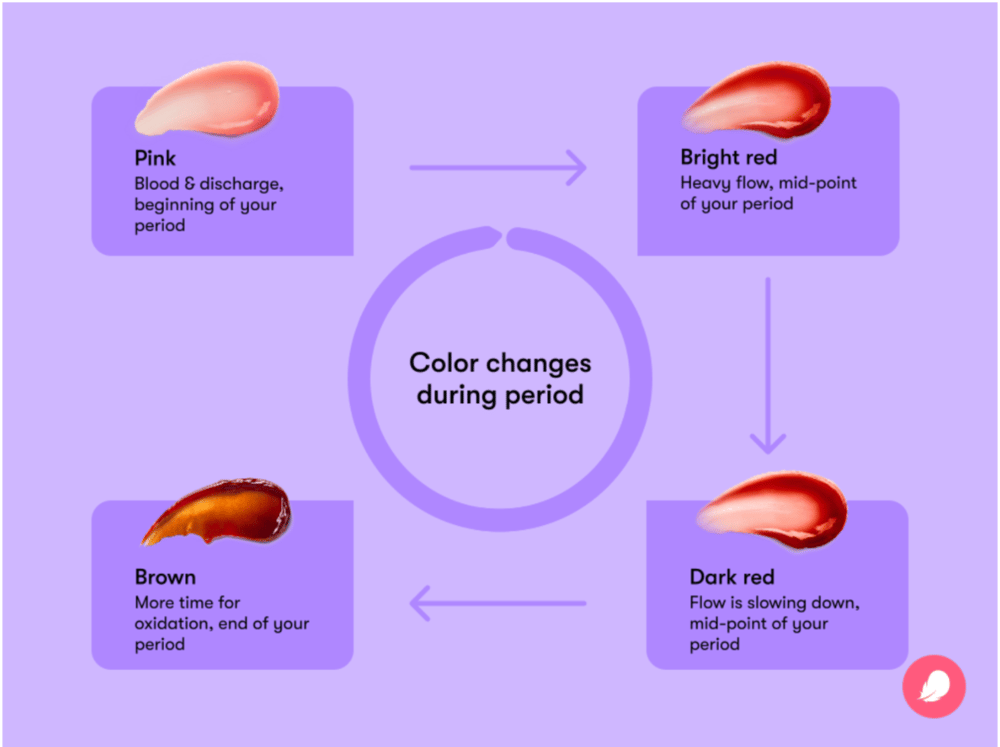
Pink blood
At the very start of your period, you may only release a little bit of blood. This can appear pink in color because your flow is light, and the red blood is being mixed with your discharge. This is very normal.
Bright red blood
Everyone’s period is different, so talking about timings can be tricky, but after around a day you might notice that your period blood color is a brighter, strawberry red. This indicates that your period is probably at its heaviest (in full flow).
Dark red blood
If your period blood is a darker scarlet red, then it could indicate that the blood has been in your body longer, giving it more time to react with oxygen. It also suggests that your flow has slowed down a little bit.
Brown blood
As your period comes to an end, it might look more brown. This might feel alarming, but fear not. It’s easily explained. At this point in your period, your blood has just had more time outside of your blood vessels, and your flow might have slowed down. This means that blood is leaving your uterus at a slower pace, giving your blood more time to react with oxygen in your body (oxidation).
Other potential discharge colors
Period blood isn’t the only thing you might find in your underwear. While the average period lasts between two and seven days, your vagina produces other fluid throughout the rest of your cycle that helps to keep you clean and healthy. This is called discharge.
The color of discharge can vary from person to person and depends on where you are in your cycle and other factors like infections. So the key is to understand your baseline. Then, it’ll be easier to know when something’s off. You can learn more about your body and your cycle using an app like Flo.
Discharge color chart

Normal discharge is usually clear or whitish and mild odored. It might feel wet and slippery, sticky and gooey, thick and creamy, or drier and more pasty. The consistency and color of your discharge can change throughout your cycle due to hormonal fluctuations.
However, the color of your discharge can also signify infection. Reach out to your doctor if your discharge is:
- Clumpy and white: This could be a sign of a yeast infection if accompanied by other symptoms like itching and irritation.
- Yellow or green: This could be a sign of an infection, especially if it’s accompanied by a foul smell.
- Gray: This could be a sign of bacterial vaginosis (BV). Another common sign of BV is a strong fishy smell.
- Pink or brown: This could just be a sign that your period is beginning or ending and a bit of blood has mixed with your discharge. However, if you also feel pain, itching, or irritation, it could be a sign of an infection.
And remember: While these color changes in your discharge could indicate one of the infections or conditions above, this isn’t an exhaustive list. It’s completely typical for your discharge to vary in color and consistency at different points in your cycle, and there are different reasons why yours might change. If you notice something isn’t quite right for you or you have any other uncomfortable symptoms, you can speak to your doctor. They’ll be able to help you with the best next step.
Tips for tracking your blood color
Using a period tracker like Flo can help you better understand your cycle and your body. You can track your cycle length and any symptoms to help you spot patterns and get used to what’s typical for you.
We are all different and unique, and our cycles are no exception to this. Flo can help you predict where you are in your cycle and what you might expect now and in the future so you can feel prepared for every period.
More frequently asked questions about period blood color
What does period blood color mean?
How bright your period blood is can indicate how fast your flow is and where you are in your cycle. As a general rule, the brighter your period blood, the faster your flow. Your blood gets darker the longer it’s outside the blood vessels as it has more time to react to oxygen. This is called oxidation and can mean your blood appears brown.
What color period blood is concerning?
While pink, red, or brown period blood generally isn’t something to worry about, you know your body best. If you notice a difference in the way your period looks or smells or you develop new uncomfortable symptoms, don’t hesitate to reach out to your doctor. They’ll be able to examine you and figure out the best next step.
Hey, I'm Anique
I started using Flo app to track my period and ovulation because we wanted to have a baby.
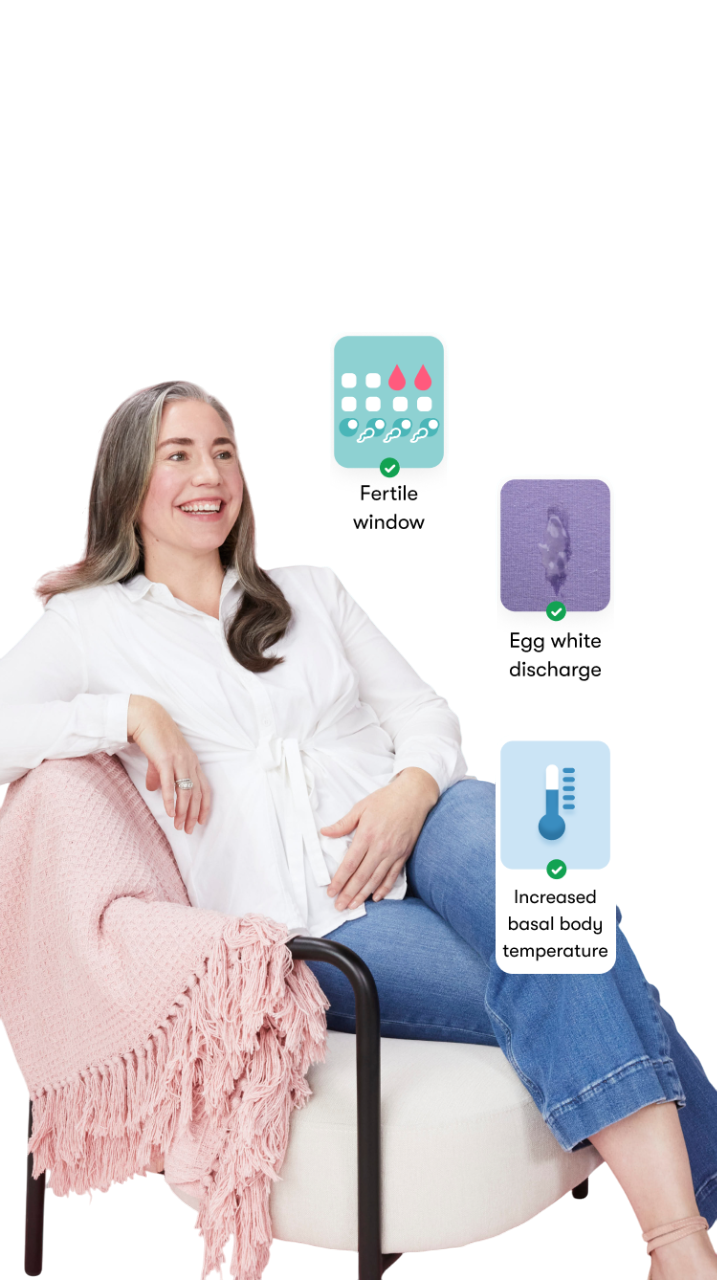

The Flo app helped me learn about my body and spot ovulation signs during our conception journey.


I vividly
remember the day
that we switched
Flo into
Pregnancy Mode — it was
such a special
moment.
Real stories, real results
Learn how the Flo app became an amazing cheerleader for us on our conception journey.
References
“Bacterial Vaginosis.” Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/3963-bacterial-vaginosis. Accessed 25 Feb. 2025.
“Brown Discharge: 4 Causes and What It Means.” Cleveland Clinic, 25 July 2022, health.clevelandclinic.org/brown-vaginal-discharge.
“Menstrual Cycle.” NHS, www.nhs.uk/conditions/periods/. Accessed 25 Feb. 2025.
“Menstrual Cycle: What’s Normal, What’s Not.” Mayo Clinic, 22 Apr. 2023, www.mayoclinic.org/healthy-lifestyle/womens-health/in-depth/menstrual-cycle/art-20047186.
“Vaginal Discharge.” NHS, www.nhs.uk/conditions/vaginal-discharge/. Accessed 25 Feb. 2025.
“Vaginal Discharge.” Cleveland Clinic, my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/4719-vaginal-discharge. Accessed 25 Feb. 2025.
“Vaginal Discharge Color: What’s Normal and What Isn’t.” Cleveland Clinic, 29 July 2022, health.clevelandclinic.org/vaginal-discharge-mean.
“What Color Is Your Blood?” Cleveland Clinic, 5 May 2022, health.clevelandclinic.org/what-color-is-blood.
“What Does the Color of Your Period Mean?” Cleveland Clinic, 28 Sep. 2020, health.clevelandclinic.org/what-does-the-color-of-your-period-mean.
“Yeast Infection (Vaginal).” Mayo Clinic, 19 Nov. 2024, www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/yeast-infection/symptoms-causes/syc-20378999.




