Today we’ll learn about different breast shapes and sizes, as well as natural breast enlargement methods and ways to reduce their size. Without further ado, let’s dive into the topic.
-
Tracking cycle
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Help Center
-
Flo for Partners
-
Anonymous Mode
-
Flo app reviews
-
Flo Premium New
-
Secret Chats New
-
Symptom Checker New
-
Your cycle
-
Health 360°
-
Getting pregnant
-
Pregnancy
-
Being a mom
-
LGBTQ+
-
Quizzes
-
Ovulation calculator
-
hCG calculator
-
Pregnancy test calculator
-
Menstrual cycle calculator
-
Period calculator
-
Implantation calculator
-
Pregnancy weeks to months calculator
-
Pregnancy due date calculator
-
IVF and FET due date calculator
-
Due date calculator by ultrasound
-
Medical Affairs
-
Science & Research
-
Pass It On Project New
-
Privacy Portal
-
Press Center
-
Flo Accuracy
-
Careers
-
Contact Us
Breast Shapes and Sizes: Everything You Need to Know


Every piece of content at Flo Health adheres to the highest editorial standards for language, style, and medical accuracy. To learn what we do to deliver the best health and lifestyle insights to you, check out our content review principles.
Types of boobs
Everyone has their own unique breast shape and size. Some people have made up classifications of breast shapes, but all of them are based on visual appearance. There is no official or medical classification for breast shape.
Here are some examples of basic varieties of breast shapes:
- Round — The breasts are equally full at the top and bottom.
- East west — The right and left breasts go from the center of the chest to the sides. The nipples often point in opposite directions.
- Side set (widely set) — The shape is similar to east west, with a wider space between the breasts.
- Teardrop — The breasts are round. The bottoms are slightly wider than the tops, characterized by very smooth lines.
- Narrow — The breasts are thin, and the nipples point down. The bottoms are fuller than the tops. The breasts are longer than they are wide.
- Asymmetrical — One breast is noticeably bigger than the other.
- Bell shape — The breasts are large, full at the bottom, and slimmer at the top.
Does your breast size change with time?
Breast shape and size is determined genetically, but they can change as a result of pregnancy and lactation, intensive workouts, and sudden weight fluctuations. There may also be noticeable changes at certain points during the menstrual cycle.
The breasts can become bigger temporarily during pregnancy or when breastfeeding. Sometimes, breast shape can be related to weight gain or sexual arousal.
Certain medications can cause breast swelling, too. Some people observe this when taking birth control pills.
Asymmetrical breasts are usually normal
No one has a perfectly symmetrical body. So it’s not surprising that the left and right breasts can vary in size, shape, volume, and location.
In 2006, the British scientific journal Breast Cancer Research published data saying that only one woman in 504 had symmetrical breasts.
Experts from Emory University School of Medicine in Atlanta, Georgia, found that the left breast is bigger than the right in 62 percent of cases.
In some people, the difference isn’t striking, whereas, in others, one breast can be a full cup size bigger than the other.
Usually, this is normal, especially in adolescent girls whose bodies are still developing.
If one breast has suddenly become much bigger than the other, it may be a good idea to consult a health care provider to rule out anything serious.

What happens to breasts after weight loss?
With regular workouts and a strict diet, many people find that their thighs and butt don’t get slimmer, but their breasts get noticeably smaller.
The explanation is simple: when the body is in a caloric deficit (meaning it’s burning more calories than it’s taking in), it starts using its fat reserves proportionally.
The breasts contain not only glandular tissue but also connective and fatty tissues, so they’re affected when the body starts burning fat reserves.
The ratio of tissues is determined genetically. In people with a lot of fat, the breasts get smaller more quickly than in people with less fat.
When working out for weight loss, strengthening the chest muscles with strength exercises can help breasts look fuller.
To maintain elasticity and prevent sagging, experts advise not losing weight too quickly, eating healthy foods, and including leafy greens and lean protein in your diet.
Can exercise change your breasts?
Breasts contain glandular, connective, and fatty tissues.
They are not a muscular organ.
Breast shape and size are determined by the amount of fat and its distribution but can also be affected by exercise.
Push-ups and weight exercises that work the pectoral muscles (for instance, chest presses) strengthen breasts, which can make them rise and look fuller.
Pull-ups, squats, and plank variations make the muscles of the back and the shoulder girdle stronger, which improves posture and brings the breasts forward.
Following a healthy diet and doing fat-burning exercises such as running, aerobics, and swimming can reduce the size of breasts.
Hey, I'm Anique
I started using Flo app to track my period and ovulation because we wanted to have a baby.
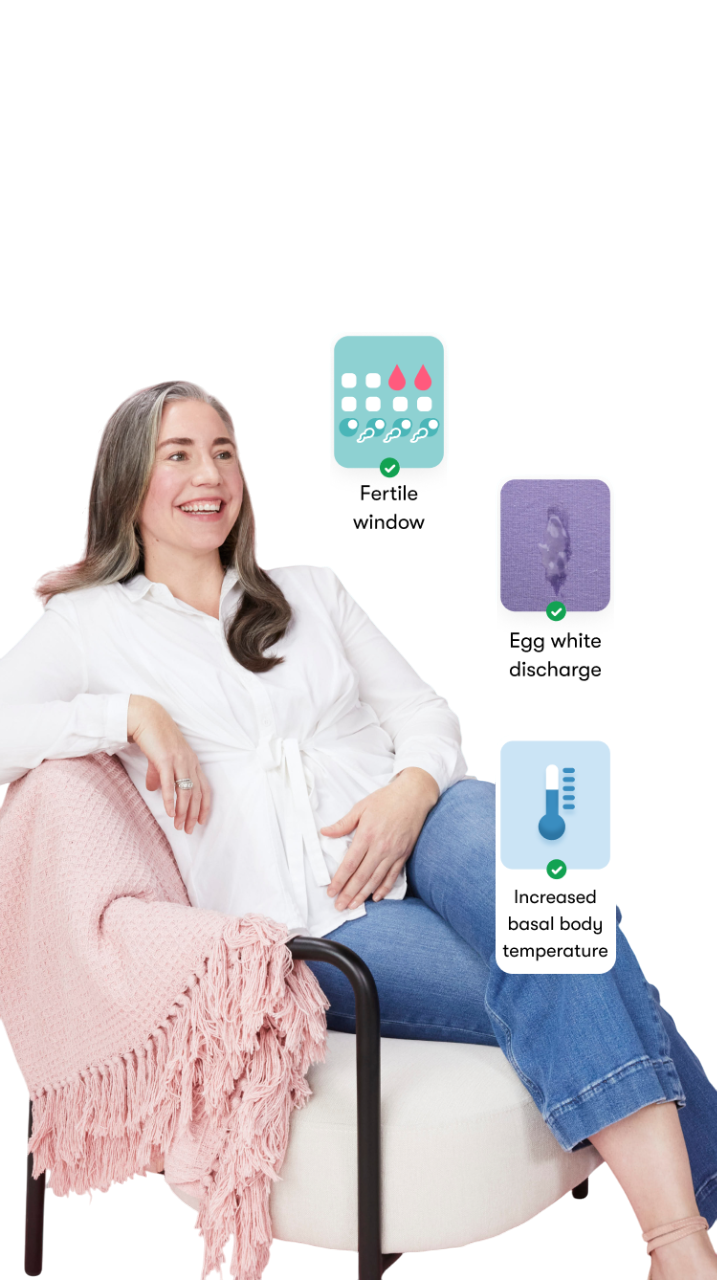

The Flo app helped me learn about my body and spot ovulation signs during our conception journey.
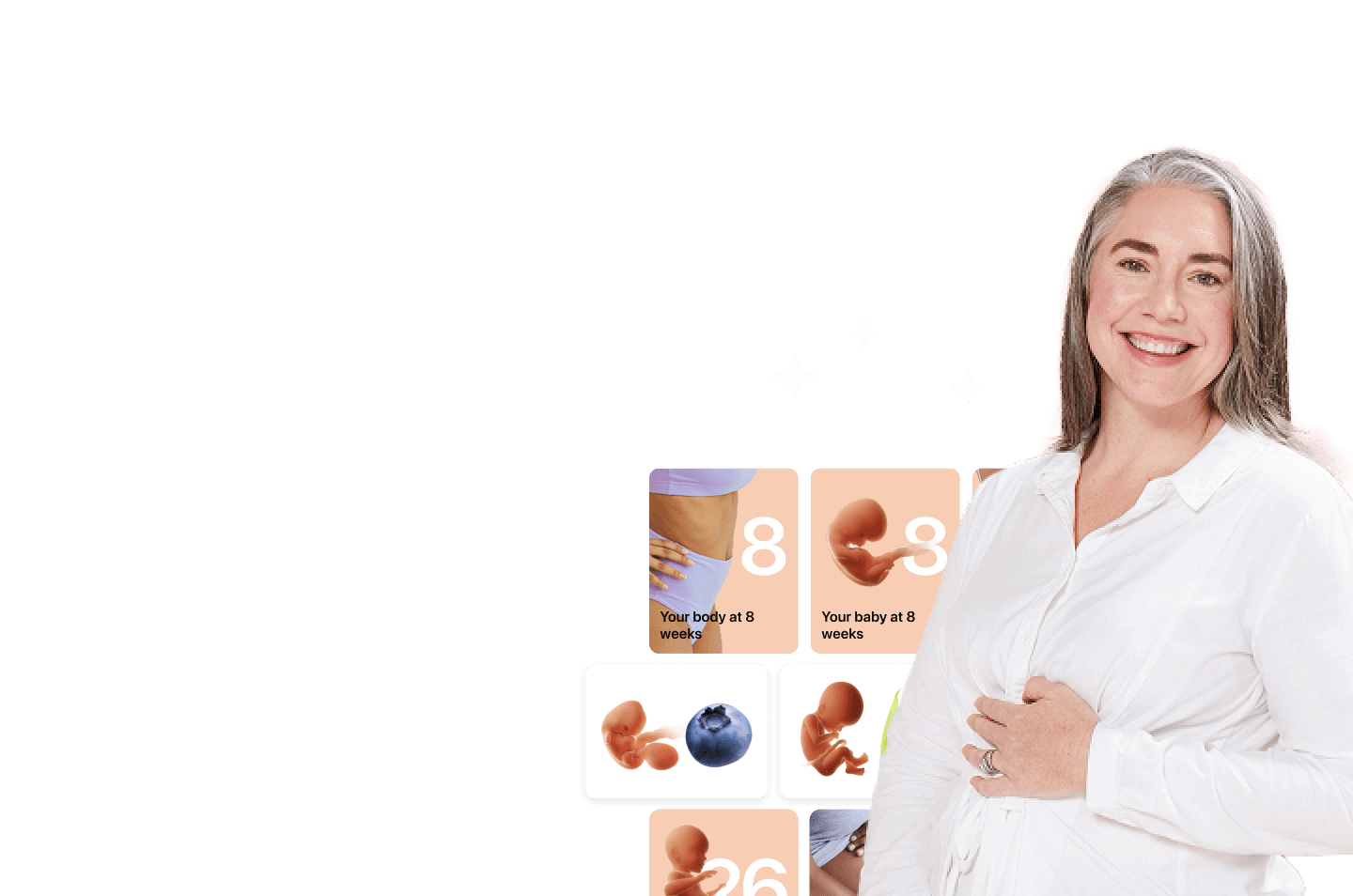
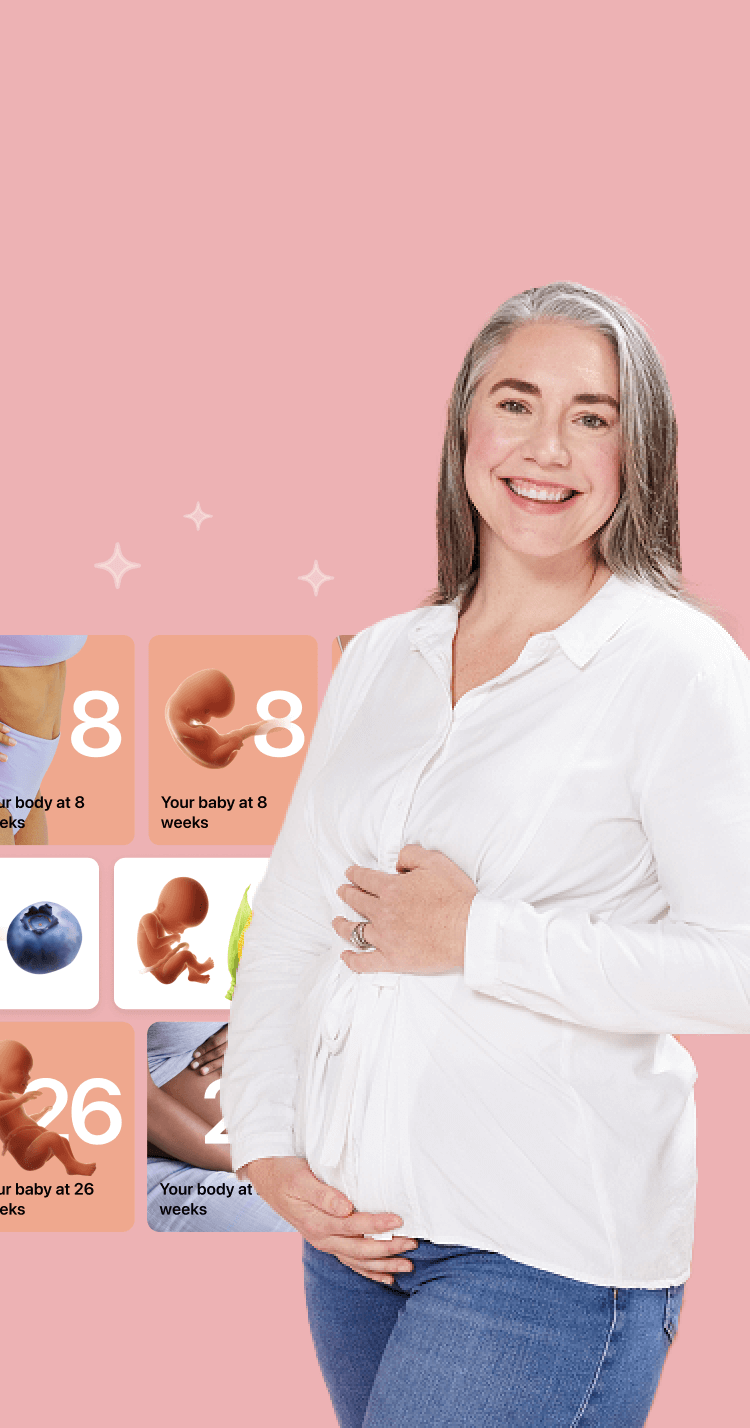


I vividly
remember the day
that we switched
Flo into
Pregnancy Mode — it was
such a special
moment.
Real stories, real results
Learn how the Flo app became an amazing cheerleader for us on our conception journey.

